News
-
 Astronomy
AstronomySome fast radio bursts come from the spiral arms of other galaxies
Tracking five brief, bright blasts of cosmic radio waves to their origins suggests their sources form quickly in regions with lots of star formation.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s what we know about the risks of serious side effects from COVID-19 vaccines
Allergic reactions, blood clots and possibly heart problems are rare and their risks don’t outweigh the benefits of getting vaccinated, experts say.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe teeth of ‘wandering meatloaf’ contain a rare mineral found only in rocks
The hard, magnetic teeth of the world’s largest chiton contain nanoparticles of santabarbaraite, a mineral never seen before in biology.
-
 Planetary Science
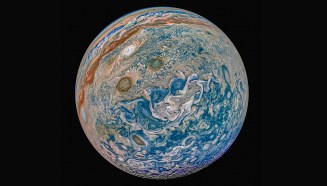
Planetary ScienceLaser experiments suggest helium rain falls on Jupiter
Compressing a hydrogen and helium mixture with lasers shows that the two elements separate at pressures found within gas giant planets.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyHunter-gatherers first launched violent raids at least 13,400 years ago
Skeletons from an ancient African cemetery bear the oldest known signs of small-scale warfare.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere are answers to 3 persistent questions about the coronavirus’s origins
Calls to double down on investigations into where SARS-CoV-2 came from — nature or a lab accident — are rising as answers remain scarce.
-
 Particle Physics
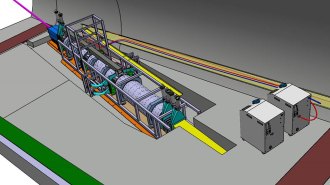
Particle PhysicsIn a first, neutrinos were caught interacting at the Large Hadron Collider
Despite the LHC’s fame, all its detectors were oblivious to neutrinos. But not anymore.
-
 Climate
ClimateThe last 30 years were the hottest on record for the United States
Typical temps across large swaths of the country are now 1 to 2 degrees Fahrenheit higher than their 20th-century averages.
-
 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePlaying brain training games regularly doesn’t boost brainpower
Comparing brain training program users with those who don’t do the mini brain workouts, scientists found no proof that the regimens boosted brainpower.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyThe oldest known tattoo tools were found at an ancient Tennessee site
Sharpened turkey leg bones may have served as tattoo needles between 5,520 and 3,620 years ago, at least a millennium earlier than previously thought.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsGray wolves scare deer from roads, reducing dangerous collisions
The predators use roads as travel corridors, creating “a landscape of fear” that keeps deer away and saves millions of dollars a year, a study finds.
By Jack J. Lee -
 Genetics
GeneticsA gene-based therapy partially restored a blind man’s vision
Light-activated proteins inserted in eye nerve cells and special goggles help the man, who lost his sight due to retinitis pigmentosa, see objects.