News
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietySTEM’s racial, ethnic and gender gaps are still strikingly large
Black and Hispanic professionals remain underrepresented in STEM, while women’s representation varies widely by STEM field, according to a new report.
-
 Health & Medicine
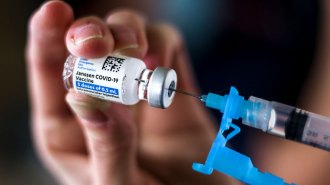
Health & MedicineU.S. pauses J&J vaccine rollout after 6 people of 6.8 million get rare blood clots
The COVID-19 vaccine’s pause is out of abundance of caution, experts say. The potentially deadly clots appear to be “extremely rare.”
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSurprisingly, humans recognize joyful screams faster than fearful screams
Scientists believed we evolved to respond to alarming screams faster than non-alarming ones, but experiments show our brains may be wired differently.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDiscarded COVID-19 PPE such as masks can be deadly to wildlife
From entanglements to ingestion, two biologists are documenting the impact of single-use masks and gloves on animals around the world.
-
 Oceans
OceansCorals’ hidden genetic diversity corresponds to distinct lifestyles
Observation and DNA analysis expose identical reef corals as distinct species with unique ecologies, suggesting much greater coral biodiversity.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow researchers can keep birds safe as U.S. wind farms expand
Tracking bald eagle abundance and migrating whooping cranes provides a clearer picture of where wind turbines could be safely built.
By Jack J. Lee -
 Climate
ClimateA trek under Thwaites Glacier’s ice shelf reveals specific risks of warm water
An underwater autonomous craft collected the first data on the chemistry of seawater eroding the icy underbelly of Antarctica’s Thwaites Glacier.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyA record-breaking, oxygen-starved galaxy may be full of gigantic stars’ shrapnel
The newly discovered galaxy may have once been home to stars more than 300 times as massive as the sun — a peek at conditions in the early universe.
By Ken Croswell -
 Anthropology
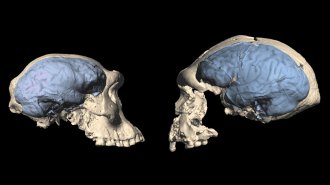
AnthropologyAncient humans may have had apelike brains even after leaving Africa
Modern humanlike brains may have evolved surprisingly late, about 1.7 million years ago, a new study suggests.
-
 Health & Medicine
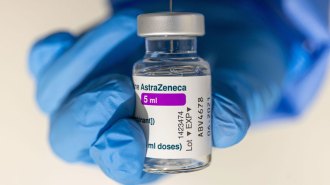
Health & MedicineAstraZeneca’s COVID-19 vaccine is tied to uncommon blood clots in rare cases
Blood clots should be listed as a possible side effect of AstraZeneca’s vaccine, but its benefits still outweigh the risks, experts say.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyPeople add by default even when subtraction makes more sense
People default to addition when solving puzzles and problems, even when subtraction works better. That could underlie some modern-day excesses.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsMuon magnetism could hint at a breakdown of physics’ standard model
After two decades, a new measurement of the muon magnetic anomaly reinforces earlier hints that its value disagrees with standard physics.