News
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceLakes of liquid water at Mars’ southern ice cap may just be mirages
In 2018, scientists found evidence for water lakes sitting beneath the southern Martian ice cap. New evidence suggests the lakes might not exist.
By Adam Mann -
 Health & Medicine
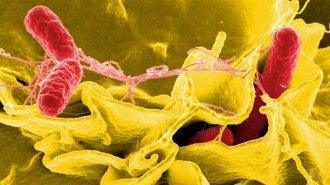
Health & MedicineHuman cells make a soaplike substance that busts up bacteria
Nonimmune cells can fight off pathogens by releasing a detergent-like molecule that dissolves bacterial membranes.
-
 Paleontology
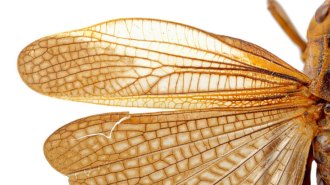
PaleontologyInsects had flashy, noise-making wings as early as 310 million years ago
The structure of a grasshopper-like insect’s fossilized wing suggests it crackled and reflected light, perhaps to attract mates or warn off predators.
-
 Health & Medicine
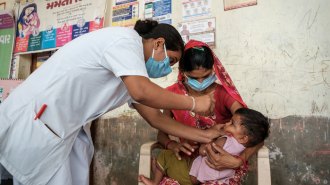
Health & MedicineMillions of kids have missed routine vaccines thanks to COVID-19
Missed shots due to the pandemic may have cut vaccination rates for measles, diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis to their lowest levels in over a decade.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWould dogs return the favor if you gave them treats? It’s complicated
An experiment in which dogs did not reciprocate food giving with humans may reveal something about the dogs, or about how science is done.
By Betsy Mason -
 Animals
AnimalsClimate change may rob male dragonfly wings of their dark spots
Less colorful, cooler wings may be advantageous to dragonflies in a warmer world. But the change could mess with the insects’ mating.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsFroghoppers are the super-suckers of the animal world
To feed on plant xylem sap, a nutrient-poor liquid locked away under negative pressure, froghoppers have to suck harder than any known creature.
-
 Climate
ClimateHurricanes may not be becoming more frequent, but they’re still more dangerous
A new study suggests that there aren’t more hurricanes now than there were roughly 150 years ago.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDogs tune into people in ways even human-raised wolves don’t
Puppies outpace wolf pups at engaging with humans, even with less exposure to people, supporting the idea that domestication has wired dogs’ brains.
-
 Earth
EarthSatellites show how a massive lake in Antarctica vanished in days
Within six days, an Antarctic lake with twice the volume of San Diego Bay drained away, leaving a deep sinkhole filled with fractured ice.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOne mutation may have set the coronavirus up to become a global menace
A study pinpoints a key mutation that may have put a bat coronavirus on the path to becoming a human pathogen, helping it better infect human cells.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyThe gap in parenting time between middle- and working-class moms has shrunk
Some well-educated mothers are spending less time with their kids than before, while some less-educated mothers are spending more, a new study shows.
By Sujata Gupta