News
-
 Physics
PhysicsAntiprotons show no hint of unexpected matter-antimatter differences
The ratio of electric charge to mass for protons mirrors that of their antimatter counterparts.
-
 Health & Medicine
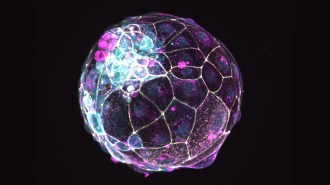
Health & Medicine‘Blastoids’ made of stem cells offer a new way to study fertility
Newly created “blastoids” could help with research on nonhormonal contraceptives and fertility treatments.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsHere’s how spider geckos survive on Earth’s hottest landscape
An analysis of the stomach contents of Misonne’s spider geckos shows there are more critters in the heart of Iran’s Lut Desert than meets the eye.
By Jude Coleman -
 Astronomy
AstronomyTwo stars’ close encounter may explain a cosmic flare that has barely faded
A brilliant outburst of light that has lasted nearly a century arose when two young stars skirted past each other, simulations suggest.
By Ken Croswell -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe coronavirus may cause fat cells to miscommunicate, leading to diabetes
Researchers are homing in on a surprising cause of high blood sugar in COVID-19 patients and possibly what to do about it.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyArctic hunter-gatherers were advanced ironworkers more than 2,000 years ago
Swedish excavations uncover furnaces and fire pits from a big metal operation run by a small-scale society, a new study finds.
By Bruce Bower -
 Climate
ClimateAfrica’s ‘Great Green Wall’ could have far-reaching climate effects
The “Great Green Wall,” a tree-planting project to stop desertification in northern Africa, could alter climate patterns in the region and beyond.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceEnceladus’ plumes might not come from an underground ocean
The celebrated plumes of Saturn’s moon Enceladus could come from pockets of watery mush in the moon’s icy shell, simulations suggest.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA 1,306-legged millipede is the first to live up to its name
Scientists have discovered the first true millipede, an elongated, threadlike creature with a whopping 1,306 legs.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe omicron variant is surging. Here’s what we’ve learned so far
Omicron is better at evading virus-attacking antibodies than previous coronavirus variants, but there are signs booster shots might help curb symptoms.
-
 Climate
ClimateVikings may have fled Greenland to escape rising seas
Vikings abandoned Greenland in the 15th century. Lower temperatures, an expanding ice sheet and rising sea levels may have played a role in their departure.
By Freda Kreier -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCOVID-19 testing is complicated right now. Here are answers to 6 big questions
There are two major categories of COVID-19 diagnostic tests. Here’s what you need to know when deciding whether to take an at-home test or head to the doctor.