News
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsSome polar bears in Greenland survive on surprisingly little sea ice
“Glacial mélange” could provide a last refuge for some bears as the Earth warms, but climate action is needed to preserve the species, researchers say.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Astronomy
AstronomyNeutrinos hint the sun has more carbon and nitrogen than previously thought
Scientists still don’t know the sun’s exact chemical composition, which is crucial for understanding the entire universe. Neutrinos will help.
By Ken Croswell -
 Animals
AnimalsHere’s why pumpkin toadlets are such clumsy jumpers
Tiny Brachycephalus frogs from southern Brazil can leap into the air but have trouble landing.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyAncient bacterial DNA hints Europe’s Black Death started in Central Asia
Archaeological and genetic data pin the origins of Europe’s 1346–1353 bubonic plague to a bacterial strain found in graves in Asia from the 1330s.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsButterflies may lose their ‘tails’ like lizards
Fragile, tail-like projections on some butterflies' wings may be a lifesaver.
By Jake Buehler -
 Astronomy
AstronomyA celestial loner might be the first known rogue black hole
The object could be the first isolated stellar-mass black hole identified in the Milky Way — or it might be an unusually heavy neutron star.
-
 Physics
PhysicsWhy even small sonic booms are more annoying in cities
Quieter sonic booms from next-generation planes could still be annoying in cities thanks to narrow streets and tall buildings, simulations suggest.
-
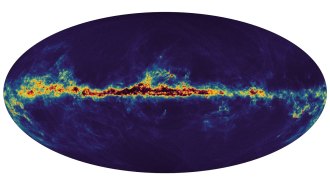 Astronomy
AstronomyNew Gaia data paint the most detailed picture yet of the Milky Way
Gaia’s new data can tell us about galaxies the Milky Way has swallowed, the young solar system and asteroids that could hit Earth.
By Asa Stahl -
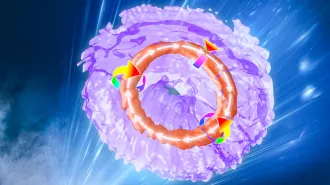 Physics
PhysicsScientists created ‘smoke rings’ of light
A swirling doughnut of light shows that vortex rings aren’t just for fluids anymore.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsQuantum physics exponentially improves some types of machine learning
It wasn’t entirely clear if quantum computers could improve machine learning in practice, but new experiments and theoretical proofs show that it can.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceSamples of the asteroid Ryugu are scientists’ purest pieces of the solar system
Samples Hayabusa2 brought to Earth from asteroid Ryugu are far fresher than similar types of meteorites that scientists have found.
By Liz Kruesi -
 Climate
ClimateAncient penguin bones reveal unprecedented shrinkage in key Antarctic glaciers
Thwaites and Pine Island glaciers are losing ice faster than any other time in the last 5,500 years. That history is written in bones and shells.
By Douglas Fox