News
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsProtons contain intrinsic charm quarks, a new study suggests
The massive quarks — counterintuitively heavier than the proton itself — might carry about 0.6 percent of a proton’s momentum.
-
 Physics
PhysicsSpiraling footballs wobble at one of two specific frequencies
Researchers simulated the path of a flying football to study how pigskins wobble and why they drift sideways.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceAsteroid impacts might have created some of Mars’ sand
Roughly a quarter of the Red Planet’s sand is spherical bits of glass forged in violent impacts, new observations reveal.
-
 Space
SpaceOver time, Betelgeuse changed color. Now it’s also lost its rhythm
A recent upset to the star’s variability and ancient records that describe the red star as yellow tell a tale of a star that is no stranger to change.
-
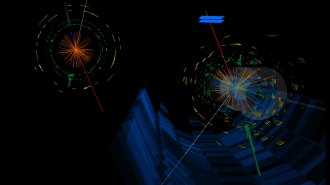 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsPhysicists spotted rare W boson trios at the Large Hadron Collider
By measuring how often triplets of particles called W bosons appear, scientists can check physics’ standard model for any cracks.
-
 Humans
HumansWhy humans have more voice control than any other primates
Unlike all other studied primates, humans lack vocal membranes. That lets humans produce the sounds that language is built on, a new study suggests.
By Asa Stahl -
 Earth
EarthThe Arctic is warming even faster than scientists realized
The Arctic isn’t just heating up two to three times as quickly as the rest of the planet. New analyses show that warming is almost four times as fast.
-
 Animals
AnimalsZoo gorillas use a weird new call that sounds like a sneezy cough
A novel vocalization made by the captive great apes may help them draw human attention.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Life
LifeSea sponges launch slow-motion snot rockets to clean their pores
Sea sponges rely on a sneezing mechanism to clear their pores, using mucus to flush out debris. This mucus provides food for other marine life.
By Jude Coleman -
 Space
SpaceHow balloons could one day detect quakes on Venus
A new study opens the door for future balloon-based missions to study the geology of other worlds.
By Freda Kreier -
 Animals
AnimalsRelocated beavers helped mitigate some effects of climate change
Along a river in Washington state, the repositioned beavers built dams that lowered stream temperatures and boosted water storage.
-
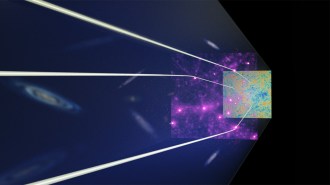 Cosmology
CosmologyScientists mapped dark matter around galaxies in the early universe
A technique used to reveal dark matter could also shed light on a disagreement about the clumpiness of matter in the cosmos.