News
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyA new seasoning smells like meat thanks to sugar — and mealworms
A spoonful of sugars could help cooked mealworms go down more easily, a potential boon for the planet.
By Anil Oza -
 Anthropology
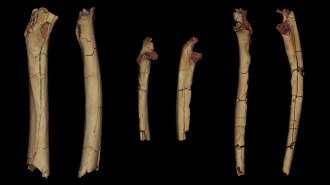
Anthropology7-million-year-old limb fossils may be from the earliest known hominid
An earlier report on one of the bones of a 7-million-year-old creature that may have walked upright has triggered scientific misconduct charges.
By Bruce Bower -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSleep deprivation may make people less generous
Helping each other is inherently human. Yet new research shows that sleep deprivation may dampen people’s desire to donate money.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Animals
AnimalsNews stories have caught spiders in a web of misinformation
Nearly half of news stories about peoples’ interactions with spiders contain errors, according to a new analysis.
By Betsy Mason -
 Earth
EarthNot one, but two asteroids might have slain the dinosaurs
A craterlike structure found off West Africa’s coast might have been formed by an asteroid impact around the same time the dinosaurs went extinct.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Animals
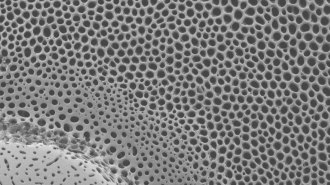
AnimalsSea urchin skeletons’ splendid patterns may strengthen their structure
“Voronoi” geometric patterns found in sea urchin skeletons yield strong yet lightweight structures that could inspire the creation of new materials.
-
 Animals
AnimalsExtreme climate shifts long ago may have helped drive reptile evolution
The end-Permian extinction left reptiles plenty of open ecological niches. But rapid climate change may be what kick-started the animals’ dominance.
By Beth Geiger -
 Life
LifeAn award-winning photo captures a ‘zombie’ fungus erupting from a fly
The winner of the 2022 BMC Ecology and Evolution photo competition captures a macabre cycle of life and death in the Peruvian Amazon.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentCommon, cheap ingredients can break down some ‘forever chemicals’
Forever chemicals, or PFAS, are harmful compounds that are very difficult to degrade. But some are no match for lye and dimethyl sulfoxide.
By Jude Coleman -
 Animals
AnimalsWhy mosquitoes are especially good at smelling you
How Aedes aegypti mosquitoes smell things is different from how most animals do, making hiding human odors from the insects more complicated.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceOort cloud comets may spin themselves to death
How icy objects from the solar system’s fringe break up as they near the sun is a long-standing mystery. One astronomer now thinks he has an answer.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe first known monkeypox infection in a pet dog hints at spillover risk
A person passed monkeypox to a dog. Other animals might be next, allowing the virus to set up shop outside of Africa for the first time.