News
-
 Physics
PhysicsZapping plastic with a laser forged tiny diamonds
The technique could be used to manufacture nanodiamonds for use in quantum devices and other applications.
-
 Earth
EarthIn 2021, a deadly volcano erupted with no warning. Here’s why
Before the Nyiragongo eruption, underground magma was already close to the surface and so didn’t trigger instruments that look for lava movement.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyHere’s the James Webb telescope’s first direct image of an exoplanet
Along with spying its first exoplanet, the James Webb telescope got its first direct spectrum of an object orbiting a star in another solar system.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA clever molecular trick extends the lives of these ant queens
Ant queens typically live much longer than their workers by blocking a key part of a molecular pathway implicated in aging, a new study suggests.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWho has the highest risk of long COVID? It’s complicated
Long COVID can look different for different people, making it difficult to pinpoint the risk factors behind it.
-
 Life
LifeAncient ‘demon ducks’ may have been undone by their slow growth
Mihirung birds grew to more than half a ton and took their time getting there. That slow growth may have been a vulnerability when humans got to Australia.
By Jake Buehler -
 Space
SpacePhysicists dispute a claim of detecting a black hole’s ‘photon ring’
A thin ring of light around a black hole, which would probe gravity in a new way, has been found, one team claims. Skeptics aren’t convinced.
-
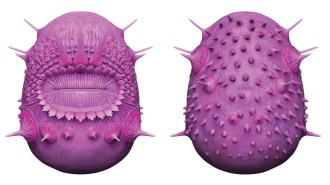 Paleontology
PaleontologyThis bizarre ancient critter has been kicked out of a group that includes humans
A wee sea creature without an anus was thought to be the oldest deuterostome. New imaging showing it had spines led to its reclassification.
By Anna Gibbs -
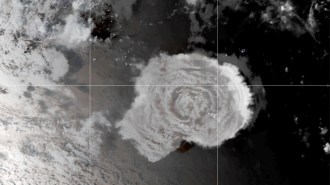 Earth
EarthThe Tonga eruption may have spawned a tsunami as tall as the Statue of Liberty
A massive undersea volcanic eruption in the South Pacific in January created a tsunami that was initially 90 meters tall, computer simulations suggest.
By Sid Perkins -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceCOVID-19 gave new urgency to the science of restoring smell
With newfound pressure from the pandemic, olfactory training and a host of other newer treatments are now getting a lot more attention.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThe James Webb telescope spotted CO2 in an exoplanet’s atmosphere
The first definitive detection of the gas on a world in another solar system paves the way for detections in planets that are more Earthlike.
-
 Space
SpaceNASA’s Artemis I mission sets the stage for our return to the moon
The launch will test many aspects of the rocket, capsule and spacesuits that will take astronauts back to the moon.