News
-
 Animals
AnimalsJumping beans’ random strategy always leads to shade — eventually
Jumping beans use randomness to maximize their chances of getting out of the sun’s heat, a new study finds.
-
 Physics
PhysicsWe could get messages back from spacecraft sent through a wormhole
A simulation of a probe sent to the other side of a wormhole shows it could send speedy messages back before the hole closes and the probe is lost.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBrain scans suggest the pandemic prematurely aged teens’ brains
A small study suggests that the COVID-19 pandemic may have aged teen brains beyond their years.
By Freda Kreier -
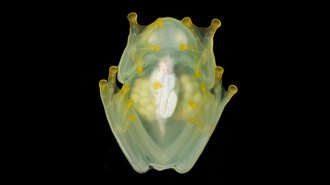 Life
LifeSleeping glass frogs hide by storing most of their blood in their liver
Glass frogs snoozing among leaves blend in by hiding almost all their red blood cells in their liver until the tiny animals wake up.
By Susan Milius -
 Space
SpaceIo may have an underworld magma ocean or a hot metal heart
New calculations support dueling ideas for what powers the ubiquitous volcanoes on the hellish surface of Jupiter’s innermost moon.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Life
LifeHere are 5 record-breaking science discoveries from 2022
The earliest surgery, fastest supercomputer and biggest single-celled bacteria were some of this year’s top science superlatives.
By Erin Wayman -
 Life
LifeSquid edit their RNA to keep cellular supply lines moving in the cold
Squid change their RNA more often in the cold, producing motor proteins that keep cellular cargo on track.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThe James Webb telescope is getting glimpses of small, far-off planets
Hints of one exoplanet atmosphere’s chemical makeup and the discovery of a planet orbiting another star are two of the telescope’s early successes.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyMysterious ichthyosaur graveyard may have been a breeding ground
Some 230 million years ago, massive dolphinlike reptiles gathered to breed in safe waters — just like many modern whales do, a study finds.
-
 Life
LifeLong genital spines on male wasps can save their lives
A male wasp’s genital spines can save his life in an encounter with a scary tree frog, a new study shows.
By Susan Milius -
 Astronomy
AstronomyThe first planet found by the Kepler space telescope is doomed
The exoplanet dubbed Kepler 1658b is spiraling toward its host star and will meet a fiery death in less than 3 million years.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceThe last vital ingredient for life has been discovered on Enceladus
The underground ocean on Saturn’s icy moon may contain phosphorus in concentrations thousands of times greater than those found in Earth’s ocean.
By Nikk Ogasa