News
-
 Climate
ClimateBaseball’s home run boom is due, in part, to climate change
Higher air temperatures led to an average of 58 more home runs each MLB season from 2010 to 2019, a study shows.
-
 Oceans
Oceans‘Jet packs’ and ultrasounds could reveal secrets of pregnant whale sharks
Only one pregnant whale shark has ever been studied. New underwater techniques using ultrasound and blood tests could change that.
-
 Animals
AnimalsInvasive yellow crazy ants create male ‘chimeras’ to reproduce
Yellow crazy ants are first known species where chimerism is required in males: Each of their cells holds DNA from just one of two genetic lineages.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyHair analysis reveals Europe’s oldest physical evidence of drug use
Analyses of human hair found in a Mediterranean cave turned up psychoactive plant substances, revealing use of hallucinogens around 3,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceVenus has almost 50 times as many volcanoes as previously thought
Where are there NOT volcanoes on Venus? A new map of the planet unveils a veritable volcanic bonanza.
-
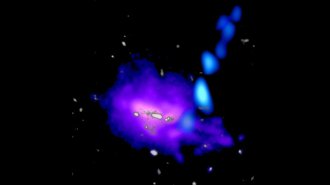 Astronomy
AstronomyA stream of cold gas is unexpectedly feeding the far-off Anthill Galaxy
The finding suggests that early galaxies might have gained more of their bulk from streams of cold gas instead of in violent galaxy collisions.
-
 Math
MathHere’s why the geometric patterns in salt flats worldwide look so similar
New research suggests the shared geometry of salt flats from Death Valley to Iran comes from fluid flows underground.
-
 Life
LifeHow some beetles ‘drink’ water using their butts
Red flour beetles, a major agricultural pest, suck water out of the air using special cells in their rear ends, a new study suggests.
By Freda Kreier -
 Physics
PhysicsThe W boson might not be heavier than expected after all
A new and improved look at the mass of the W boson is in close alignment with theory, but it doesn’t negate an earlier, controversial measurement.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyWhat did Homo sapiens eat 170,000 years ago? Roasted, supersized land snails
Charred shell bits at an African site reveal the earliest known evidence of snail-meal prep, suggesting ancient humans cooked and shared the mollusks.
By Bruce Bower -
 Planetary Science
Planetary SciencePlanets without stars might have moons suitable for life
Thanks to gravitational squeezing by their host planets, some moons of rogue planets could stay warm for over a billion years, simulations suggest.
By Bas den Hond -
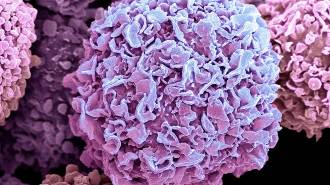 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA new battery starves cancer cells of oxygen in mice
When a self-charging battery is placed on a mouse’s tumor and combined with anticancer drugs, it reduced tumor size by 90 percent.