News
-
 Chemistry
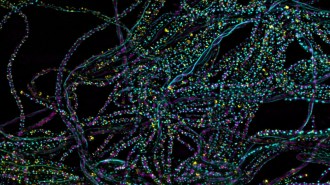
ChemistryOne photon is all it takes to kick off photosynthesis
A single particle of light is the spark that begins the process of turning light to chemical energy in photosynthetic bacteria, a new study confirms.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyJupiter-sized planets are very rare around the least massive stars
A six-year search of 200 nearby low-mass red dwarf stars found no Jupiter-like planets, boosting the standard theory for how such planets form.
By Ken Croswell -
 Animals
AnimalsCamouflaging wheat with a wheat smell could be a new approach to pest control
Wheat fields coated in wheat germ oil confuse the noses of mice, reducing seed loss by more than 60 percent, a new study finds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBowhead whales may have a cancer-defying superpower: DNA repair
Bowhead whale cells repair damaged DNA exceptionally well, an ability that could prevent cancer and help the marine mammals live for centuries
By Meghan Rosen -
 Space
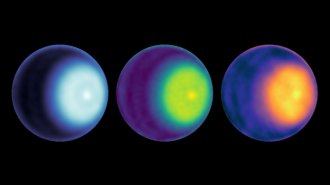
SpaceA cyclone has been spotted swirling over Uranus’ north pole for the first time
Voyager 2 hinted at a cyclone at Uranus’ south pole. Now Earth-based observations give the first direct evidence of a storm at the ice giant’s north pole.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyAn old perfume bottle reveals what some ancient Romans smelled like
Chemical analyses reveal that an unopened flask of perfume from 2,000 years ago contained patchouli, a common ingredient in modern perfumes.
-
 Climate
ClimateWildfire smoke is blanketing the U.S. East Coast. It won’t be the last time
Climate change will continue to exacerbate fire risk across the world’s boreal forests, making events like the dangerous smoke over the U.S. East Coast more common.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentRising groundwater threatens to spread toxic pollution on U.S. coastlines
Sea level rise is pushing groundwater into shallower layers of earth, threatening to spread hazardous chemicals from contaminated soils.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Environment
EnvironmentSurviving a drought may help forests weather future dry spells
Climate change is making droughts more intense and frequent, but conifer forests have a trick up their sleeve, airplane and satellite data show.
-
 Planetary Science
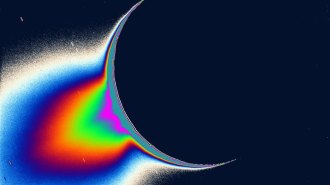
Planetary ScienceJWST captured Enceladus’ plume spraying water nearly 10,000 kilometers into space
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope reveals the rate at which Saturn’s moon Enceladus spews water and where that water ends up.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyThese ancient flutes may have been used to lure falcons
Seven bird-bone flutes unearthed from a site in northern Israel are about 12,000 years old and may have been used as bird calls.
By Sid Perkins -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTaurine slows aging in mice. Will it ever work for people?
The amino acid taurine — found in meats, produced by the body and common in energy drinks — may have a role in health and aging, a new study suggests.