News
-
 Animals
AnimalsHuge relatives of white sharks lived earlier than thought
Lamniform sharks such as great whites and tiger sharks are famous for their size. The first such giants evolved 15 million years earlier than thought.
By Jake Buehler -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGLP-1 drugs failed to slow Alzheimer’s in two big clinical trials
Tantalizing results from small trials and anecdotes raised hopes that drugs like Ozempic could help. Despite setbacks, researchers aren’t giving up yet.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyDrought may have doomed the ‘hobbits’ of Flores
Stalagmite data suggest Homo floresiensis faced prolonged drought that stressed both them and their prey, contributing to their disappearance.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA CDC panel has struck down universal newborn hepatitis B vaccination
A reshaped vaccine committee voted to scale back newborn hepatitis B shots despite decades of data showing the birth dose is safe, effective and vital.
-
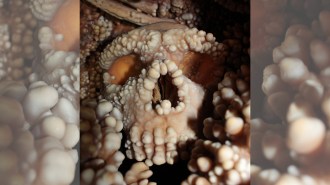 Anthropology
AnthropologyBig Neandertal noses weren’t made for cold
Tiny cameras threaded inside a Neandertal skull provide evidence that their big noses were not an adaptation to cold climates.
By Tom Metcalfe -
 Animals
AnimalsHow male seahorses tap into their mothering side
By studying the genes responsible for the seahorse’s brood pouch, researchers uncovered a new route to “motherhood.”
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyNanotyrannus is still not a teenage T. rex
Nanotyrannus wasn’t a juvenile T. rex but a petite adult of a separate species, a new study of fossil hyoid bones finds, bolstering a recent report.
-
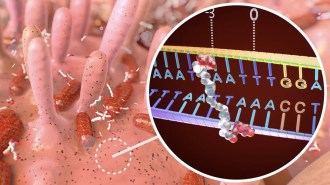 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow a bacterial toxin linked to colon cancer messes with DNA
A closeup look at colibactin’s structure reveals chemical motifs that guide its mutation-wreaking “warheads” to specific stretches of DNA.
By Elise Cutts -
 Psychology
PsychologyChatbots spewing facts, and falsehoods, can sway voters
Chatbots that dole out fact-laden arguments can sway voters. Those facts don’t have to be true.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Earth
EarthA volcanic eruption might have helped bring the Black Plague to Europe
A volcanic eruption may have triggered a deadly chain of events that brought the Black Plague to Europe in the 14th century.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAncient DNA reveals China’s first ‘pet’ cat wasn’t the house cat
The modern house cat reached China in the 7th century. Before that, another cat — the leopard cat — hunted the rodents in ancient Chinese settlements.
-
 Humans
HumansAncient southern Africans took genetic evolution in a new direction
An ancient, shared set of human-specific genes underwent changes in a geographically isolated population after around 300,000 years ago, scientists say.
By Bruce Bower