News
-
 Earth
EarthAn underwater volcano off Oregon didn’t erupt in 2025 after all. Why not?
Data from Axial, the most-monitored underwater volcano, are helping geophysicists hone eruption predictions. For Axial, 2026 is their next bet.
-
 Life
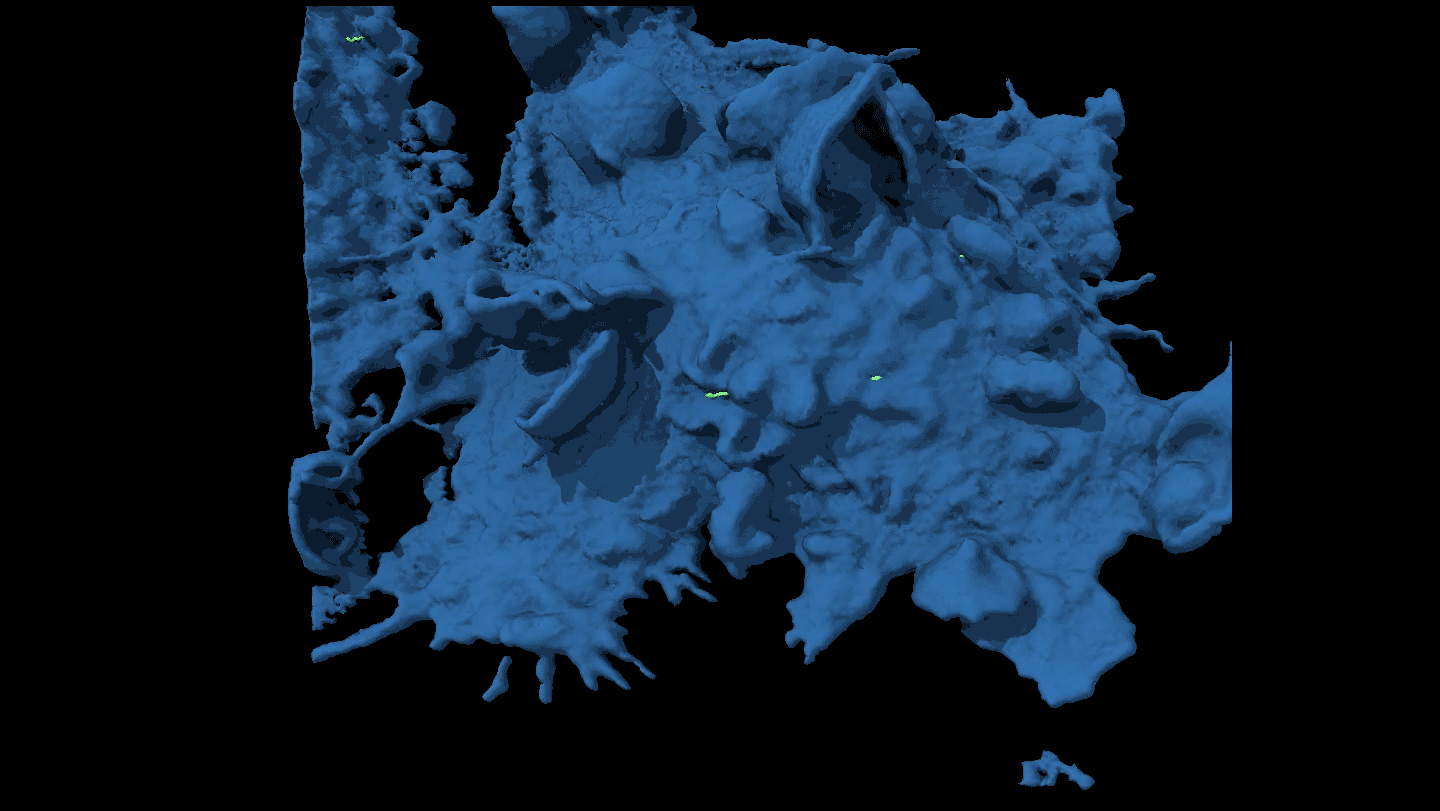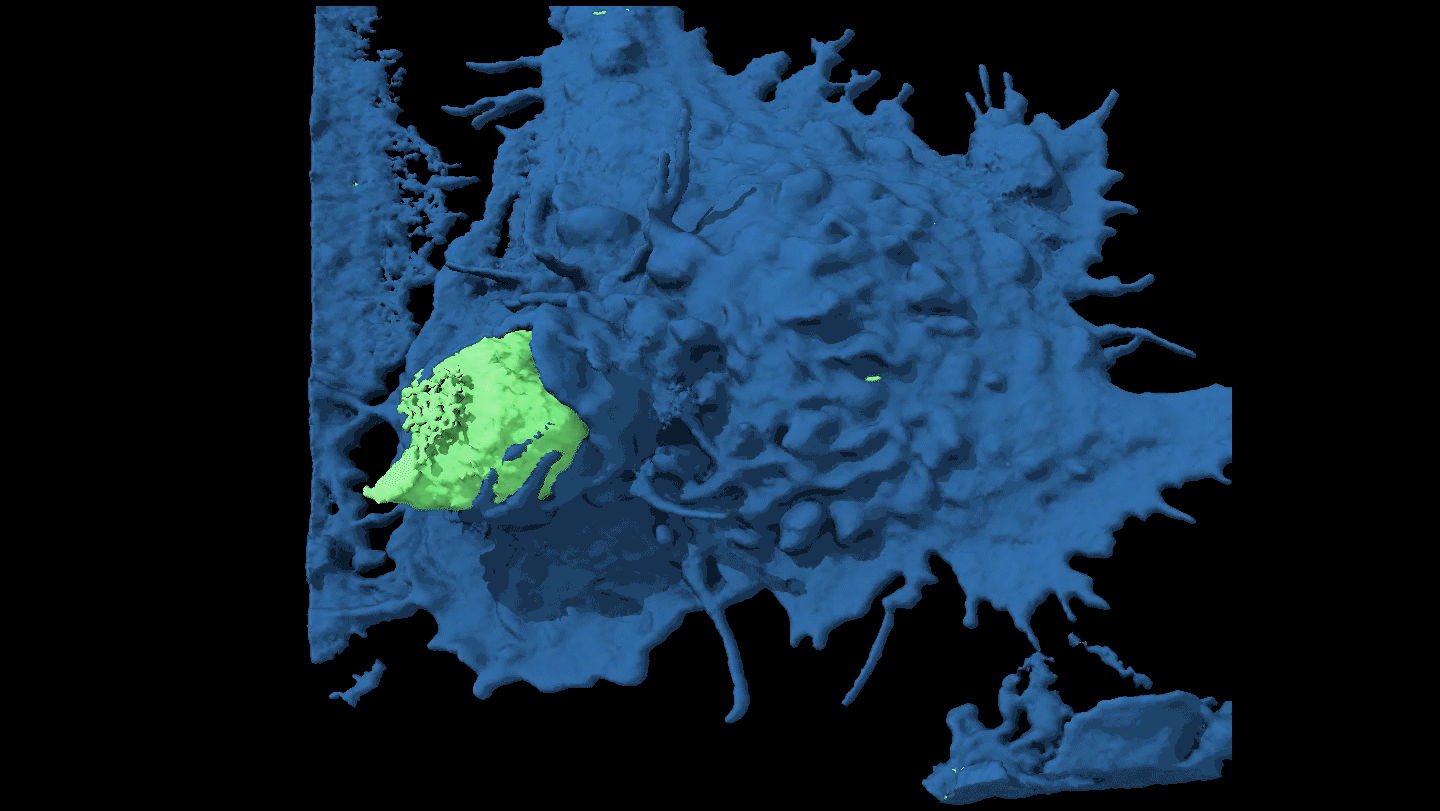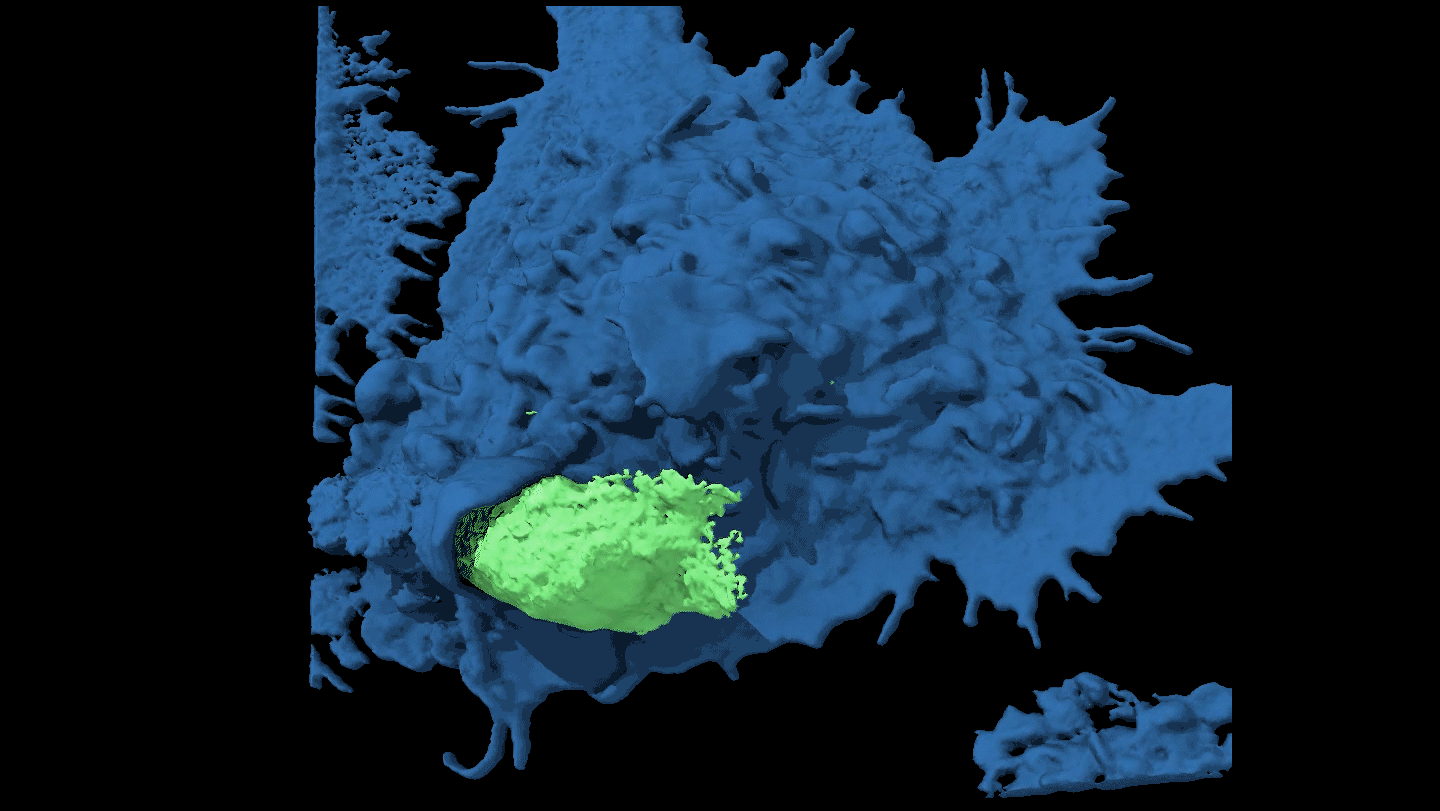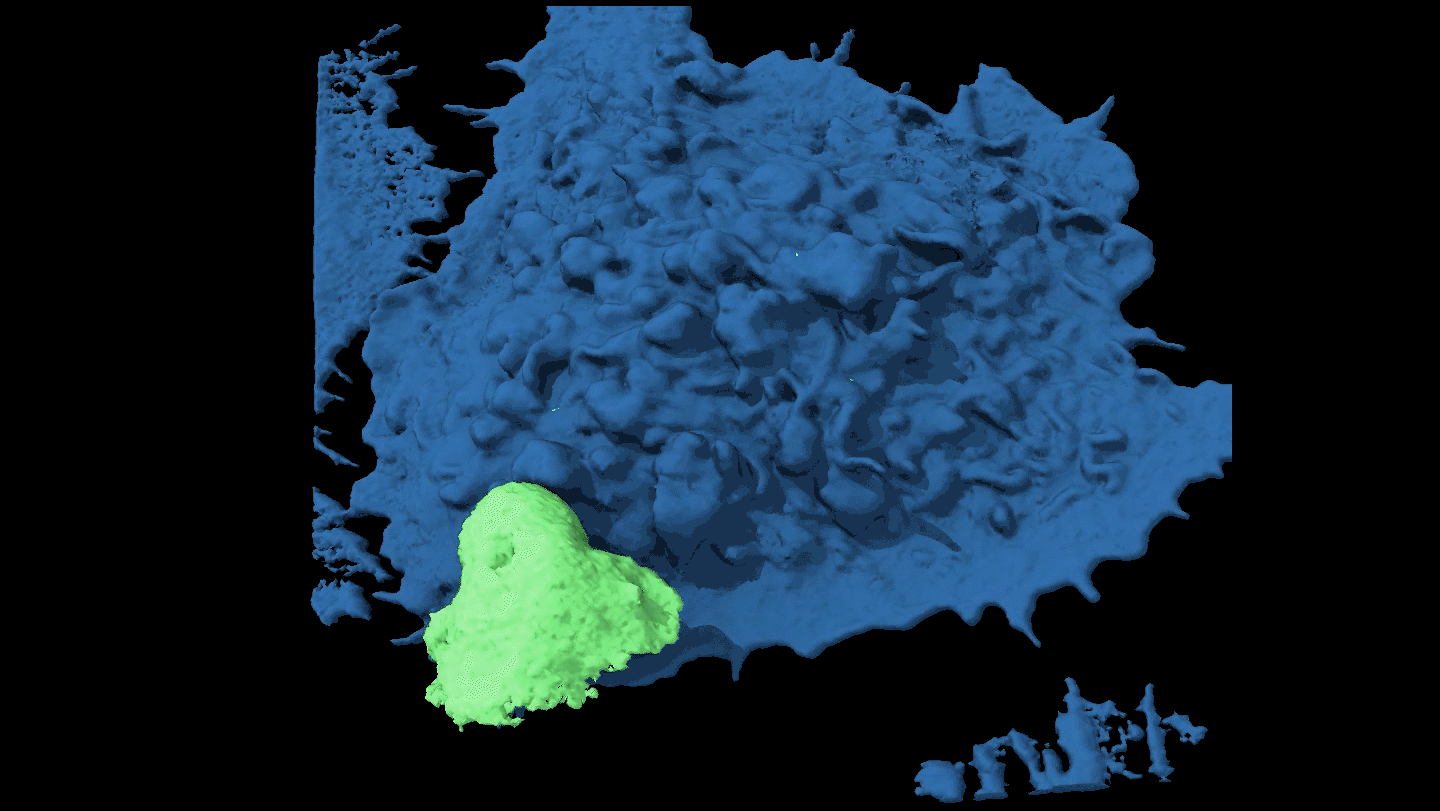
LifeWatch a cancer cell evade capture
By moving around, some cancer cells force attacking immune cells to just nibble at the edges rather than engulf them completely.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceAn asteroid could hit the moon in 2032, scattering debris toward Earth
Researchers are keeping an eye on the building-sized asteroid 2024 YR4, which has a 4 percent chance of hitting the moon seven years from now.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Astronomy
AstronomyNew Hubble images may solve the case of a disappearing exoplanet
A massive collision between two asteroid-sized bodies around a nearby star offers a rare look at the violent process of planetary construction.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThis newfound cascade of events may explain some female gut pain
Gut problems like irritable bowel syndrome are often worse in women. A mouse study reveals a pain pathway involving estrogen, gut cells and bacteria.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyA new hunt for an Earth analog begins
The Terra Hunting Experiment will track the wobbles of dozens of stars nightly for years in the most focused hunt yet for an Earth twin.
-
 Microbes
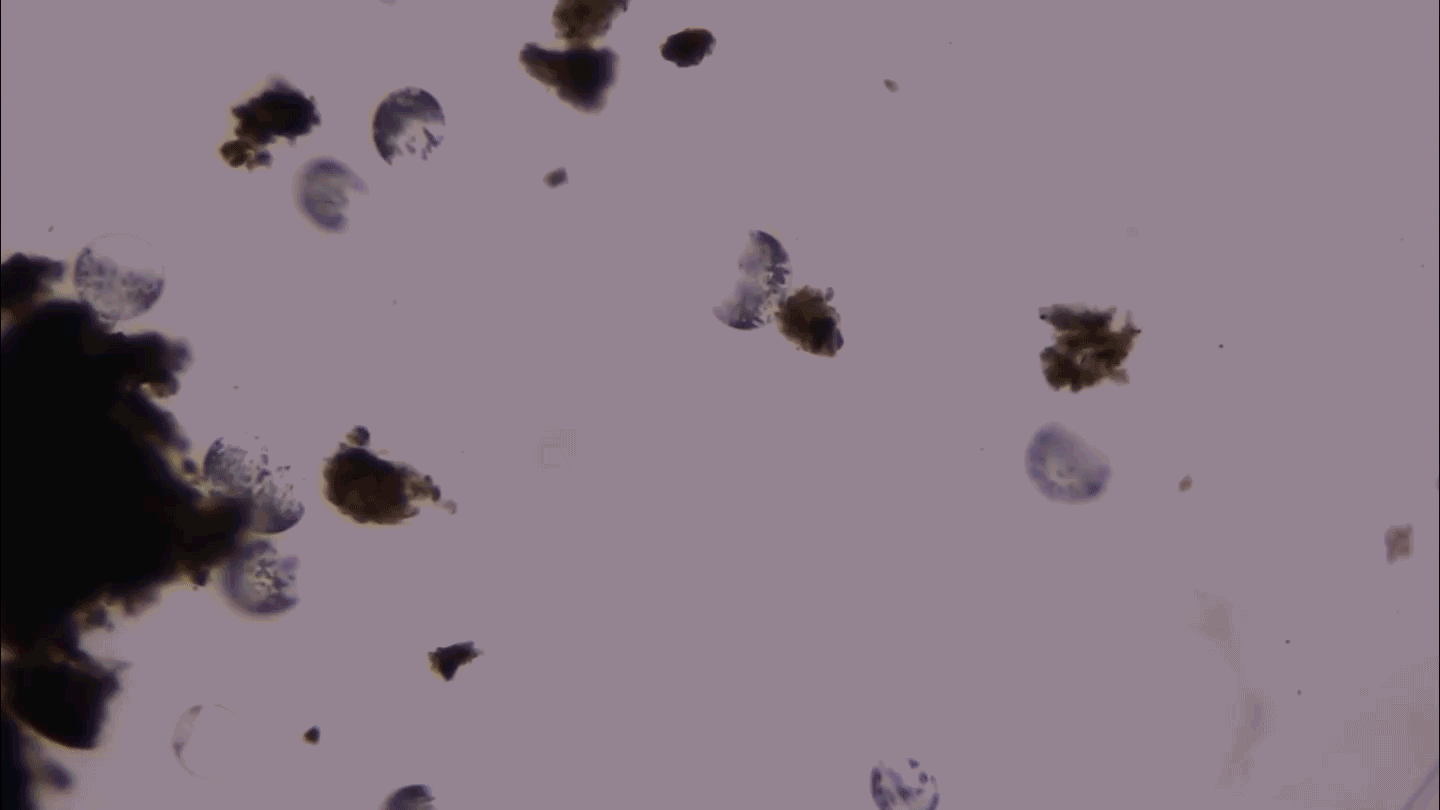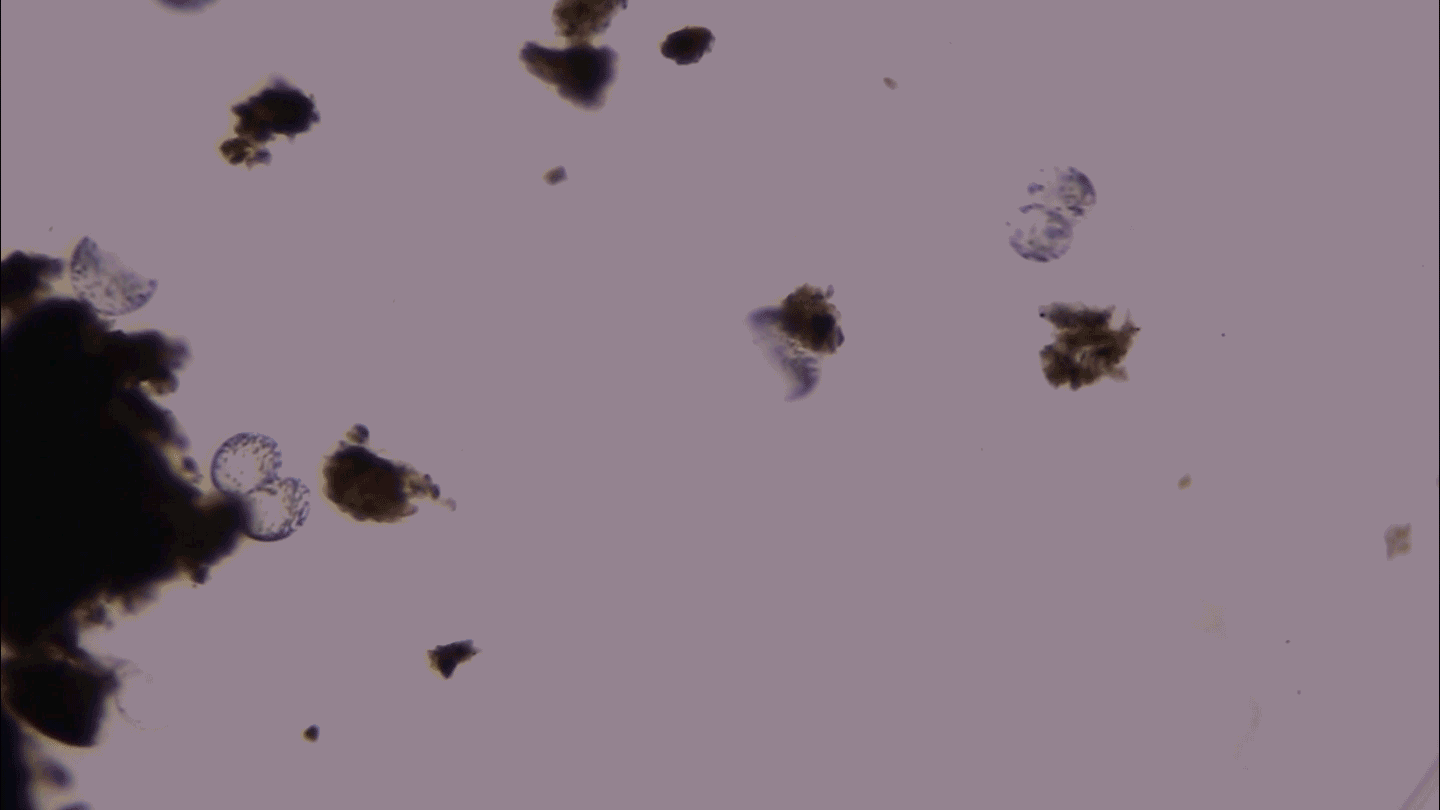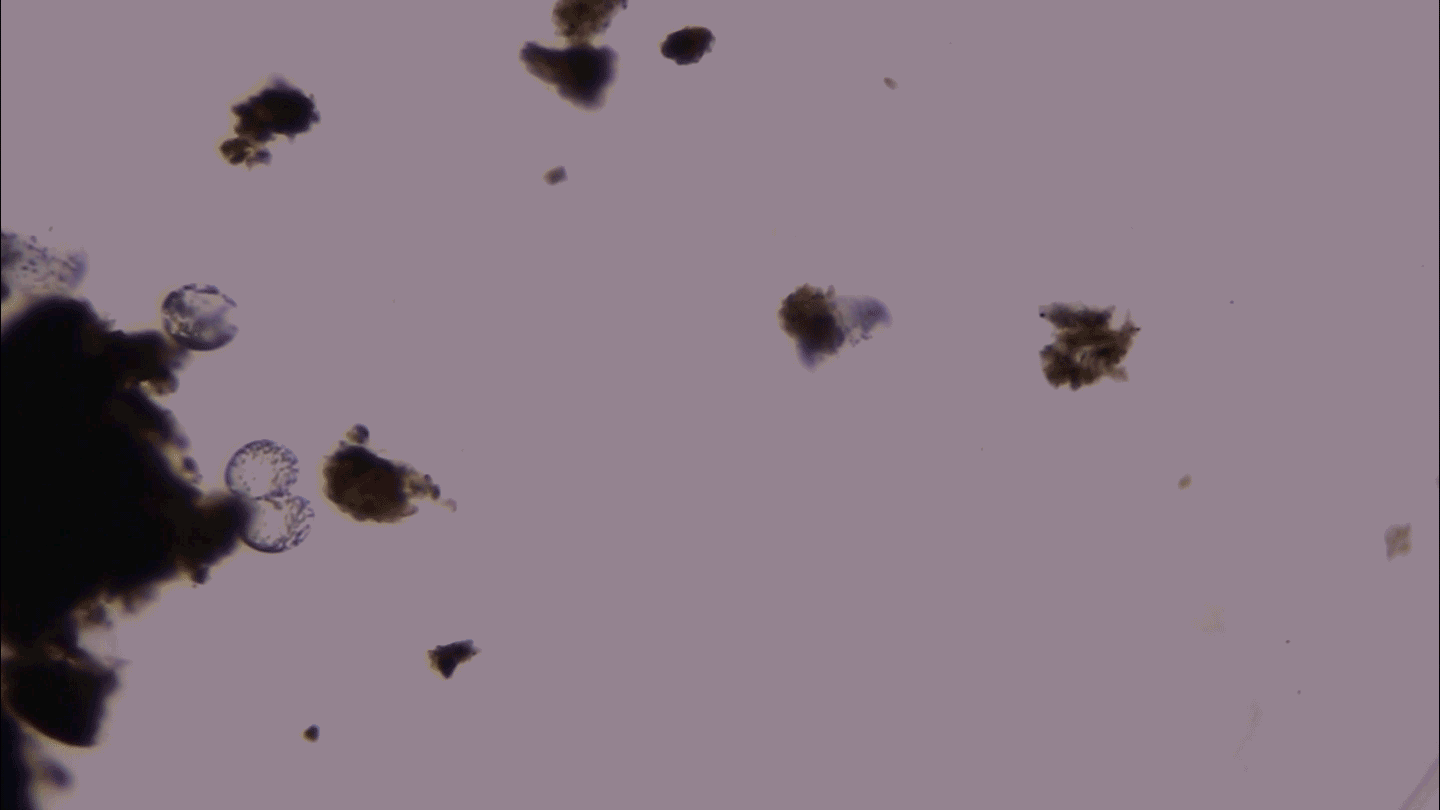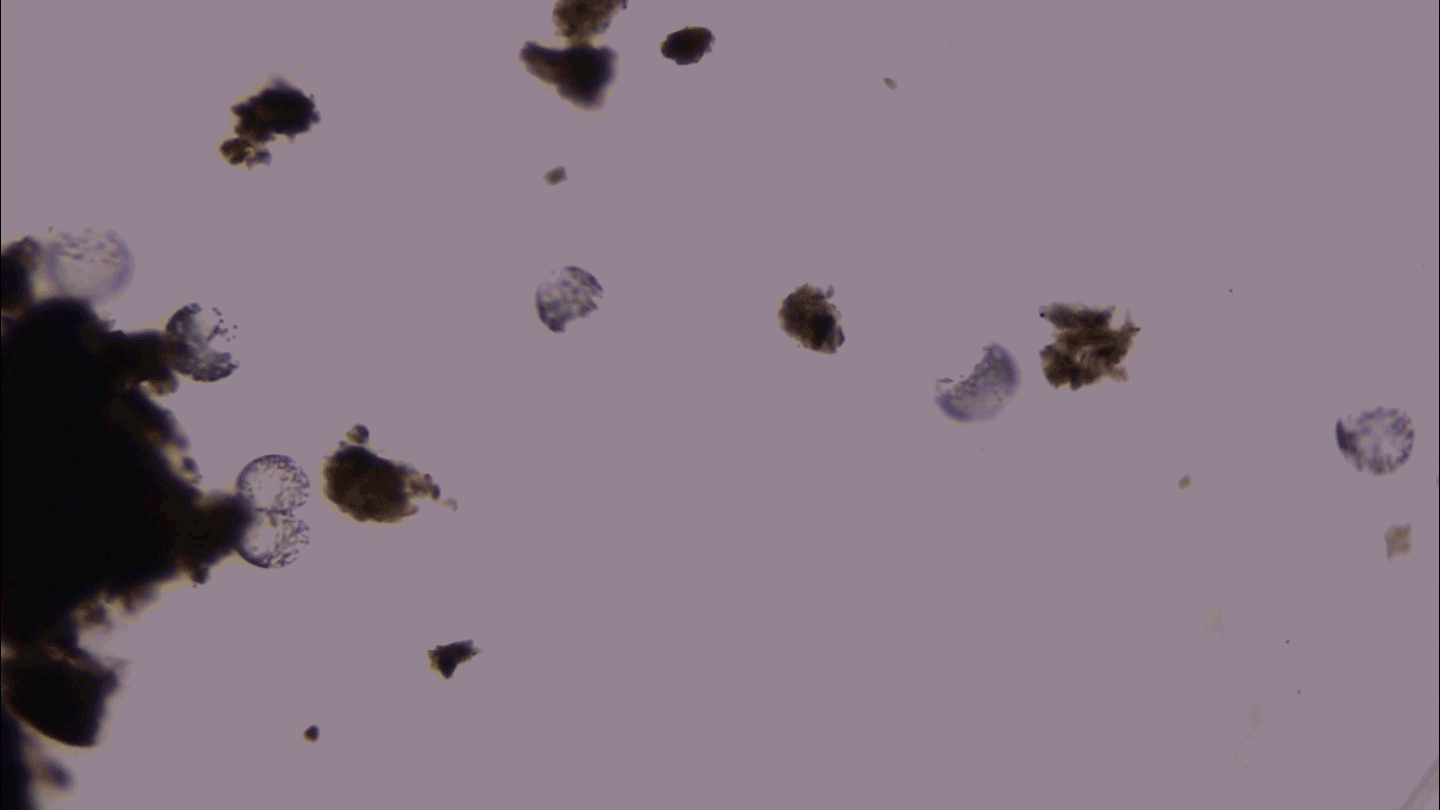
MicrobesThis giant microbe organizes its DNA in a surprising way
3-D microscopy shows that the giant bacterium Thiovulum imperiosus squeezes its DNA into peripheral pouches, not a central mass like typical bacteria.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsAncient DNA rewrites the tale of when and how cats left Africa
Cats were domesticated in North Africa, but spread to Europe only about 2,000 years ago. Earlier reports of “house” cats were wild cats.
By Jake Buehler -
 Astronomy
AstronomyDark matter ‘nuggets’ could explain the Milky Way’s mysterious glow
A mysterious excess of far-ultraviolet light seen across the Milky Way could come from the annihilation of clumpy dark matter.
-
 Tech
TechMosquitoes use it to suck blood. Researchers used it to 3-D print
A mosquito proboscis repurposed as a 3-D printing nozzle can print filaments around 20 micrometers wide, half the width of a fine human hair.
By Payal Dhar -
 Earth
EarthEarly Earth’s belly held onto its water
When the early Earth’s magma ocean crystallized 4.4 billion years ago, the deep mantle trapped an ocean’s worth of water, scientists say.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBats might be the next bird flu wild card
Finding that vampire bats along Peru’s coast carried H5N1 antibodies raises concerns that multiple bat species could become reservoirs for the virus.
By Jane Qiu