News
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s why pain might last after persistent urinary tract infections
Experiments in mice reveal that the immune response to a UTI spurs nerve growth in the bladder and lowers the pain threshold.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceThe desert planet in ‘Dune’ is plausible, according to science
Humans could live on the fictional planet Arrakis from Dune but (thankfully) no giant sandworms would menace them.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGiant tortoise migration in the Galápagos may be stymied by invasive trees
An invasion of Spanish cedar trees on Santa Cruz Island may block the seasonal migration routes of the island's giant tortoise population.
By Jake Buehler -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMore than 1 billion people worldwide are now estimated to have obesity
A new analysis suggests that the prevalence of obesity has doubled in women, tripled in men and quadrupled in children and adolescents from 1990 to 2022.
-
 Climate
ClimateWaterlogged soils can give hurricanes new life after they arrive on land
New studies show that the long-hypothesized “brown ocean effect” is real, helping to refuel 2018’s Hurricane Florence and other storms after landfall.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceOdysseus’ historic moon mission comes to an end
Odysseus downloaded data from all payloads before going to sleep February 28. The cold lunar night proved fatal to efforts to reawaken the lunar lander.
By Adam Mann -
 Genetics
GeneticsA genetic parasite may explain why humans and other apes lack tails
Around 25 million years ago, a stretch of DNA inserted itself into an ancestral ape’s genome, an event that might have taken our tails away.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe Brazilian flea toad may be the world’s smallest vertebrate
Brazilian flea toads are neither a flea nor a toad, but they are almost flea-sized. The frogs are small enough to fit on a pinkie fingernail.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSnake venom toxins can be neutralized by a new synthetic antibody
A lab-made protein protected mice from lethal doses of paralyzing toxins found in a variety of snakes, a new study reports.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Plants
PlantsOn hot summer days, this thistle is somehow cool to the touch
In hot Spanish summers, the thistle Carlina corymbosa is somehow able to cool itself substantially below air temperature.
-
 Plants
PlantsAncient trees’ gnarled, twisted shapes provide irreplaceable habitats
Traits that help trees live for hundreds of years also foster forest life, one reason why old growth forest conservation is crucial.
By Jake Buehler -
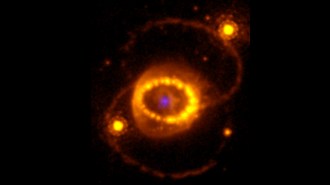 Astronomy
AstronomyJWST spies hints of a neutron star left behind by supernova 1987A
Signs of highly ionized atoms in dusty clouds at SN 1987A’s explosion site suggest a powerful source of X-rays — likely a neutron star — lurks within.
By Adam Mann