News in Brief
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOld drug reduces herpes symptoms, spread in animal tests
The antidepressant tranylcypromine might also work as antiviral against herpes, animal studies suggest.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Astronomy
AstronomyStarlight robs galaxy of stellar ingredients
Light from newborn stars drives gas out of a distant galaxy, a process that may prevent future stars from being born.
-
 Animals
AnimalsVulture guts are filled with noxious bacteria
Vultures’ guts are chock-full of bacteria that sicken other creatures.
-
 Physics
PhysicsMaterial borders support unusually warm electronic superhighways
The interface between a conductive wafer and an iron-containing film is a high-temperature superconductor, which transmits electrons without resistance.
By Andrew Grant -
 Cosmology
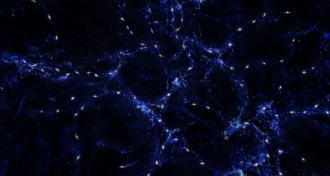
CosmologyGalaxies may be aligned across 1 billion light-years
Powerful plasma jets from cores of galaxies seem to mysteriously align with one another and hint at an unknown mechanism shaping galaxy groups.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAfter injury, estrogen may shield the brain
Estrogen helps to prevent some of the chronic inflammation that occurs after brain injury.
-
 Life
LifeNorovirus can play protective role in mice
In mice, viral infection can help intestines develop, strengthen immune system.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAreas people like to be caressed match up with nerve fibers
A caress in a sweet spot at the right speed activates nerve fibers tied to social touch.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMold may mean bad news for the brain
Living with mold isn’t good for your lungs. A study in mice shows that mold exposure may also cause inflammation that is bad for the brain.
-
 Planetary Science
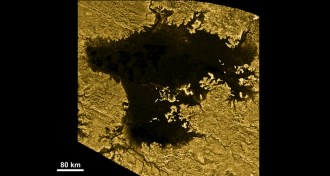
Planetary ScienceCassini maps depths of Titan’s seas
NASA’s Cassini spacecraft finds that some methane seas on Titan extend more than 200 meters beneath the Saturnian moon’s surface.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentDDT lingers in Michigan town
Decades after a plant manufacturing DDT shut down in Michigan, the harmful insecticide is still found in neighboring birds and eggs.
By Beth Mole -
 Life
LifeIguanas’ one-way airflow undermines usual view of lung evolution
Simple-looking structures create sophisticated one-way air flow in iguana lungs, undermining old scenarios of lung evolution.
By Susan Milius