News in Brief
-
 Life
LifeAsteroid barrage, ancient marine life boom not linked
Impacts from asteroid debris probably didn’t trigger the boom in marine animal diversity around 471 million years ago during the Great Ordovician Biodiversification Event.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDesert ants look to the sky, rely on memory to navigate backward
Desert ants appear to use a combination of visual memory and celestial cues to make it back to the nest walking butt-first, researchers find.
-
 Climate
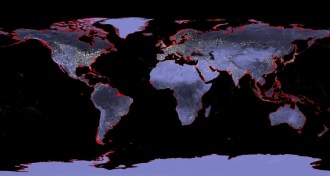
ClimateEarth’s last major warm period was as hot as today
Sea surface temperatures today are comparable to those around 125,000 years ago, a time when sea levels were 6 to 9 meters higher, new research suggests.
-
 Climate
ClimateMonsoon deluges turned ancient Sahara green
The ancient Sahara Desert sprouted trees and lakes for thousands of years thanks to intense rainfall.
By Bruce Bower -
 Tech
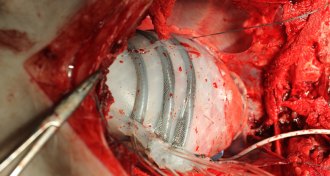
TechHeart-hugging robot does the twist (and squeeze)
A robotic sleeve that slips around the heart mimics the heart’s natural movement, squeezing and twisting to pump blood in pigs. If it works in humans, it could buy time for heart failure patients awaiting a transplant.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Life
LifeHere’s how earwax might clean ears
Science seeks inspiration in earwax for dreams of self-cleaning machinery.
By Susan Milius -
 Materials Science
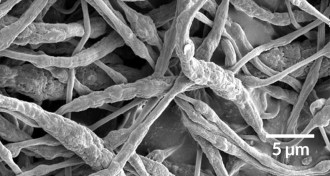
Materials ScienceNew ‘smart’ fibers curb fires in lithium-ion batteries
To stifle battery fires, scientists create component with heat-release flame retardant.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceThe moon is still old
New analysis of moon rocks points to our satellite forming about 4.51 billion years ago, roughly 60 million years after the start of the solar system.
-
 Computing
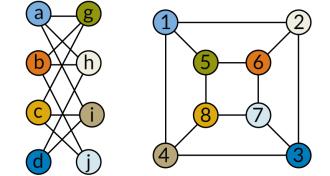
ComputingRetracted result on network equivalence reinstated
Graph isomorphism result still stands, despite error.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyMilky Way’s black hole may hurl galactic spitballs our way
Gas blobs formed in the wake of stars shredded by the black hole in the center of the galaxy could pass within several hundred light-years of Earth on their way to intergalactic space.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsDark matter still missing
The XENON100 experiment found no evidence of an annually varying dark matter signal.
-
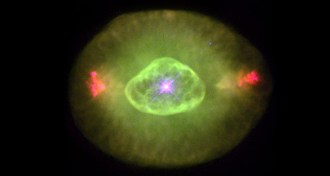 Astronomy
AstronomyEarliest galaxies got the green light
Galaxies in the early universe might have emitted lots of green light, powered by large populations of stars much hotter than most found today.