News in Brief
-
 Archaeology
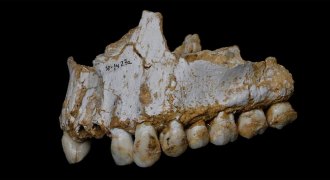
ArchaeologyAncient dental plaque tells tales of Neandertal diet and disease
Researchers have reconstructed the diet and disease history of ancient Neandertals.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsTriplet of high-energy neutrinos detected from unknown source
The IceCube Neutrino Observatory spotted three neutrinos within 100 seconds that seem to have come from the same place in the sky.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMicrocephaly, other birth defects are on the rise since Zika’s arrival
The rate of certain birth defects is much higher in babies born to Zika-infected mothers in the United States, the CDC reports.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyHydrogen volcanoes might boost planets’ potential for life
Volcanoes that spew hydrogen could increase the number of potentially habitable planets in the universe.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceSaturn’s ‘Death Star’ moon may not conceal ocean after all
A lack of cracks on Mimas suggests that the icy moon of Saturn doesn’t conceal a subsurface ocean of liquid water.
-
 Genetics
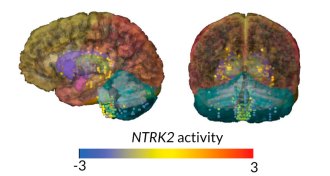
GeneticsHuman genes often best Neandertal ones in brain, testes
Differing activity of human and Neandertal versions of genes may help explain health risks.
-
 Life
LifeHowler monkeys may owe their color vision to leaf hue
Better color vision gives howler monkeys an edge at finding food.
-
 Life
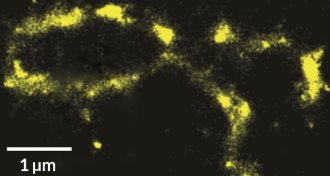
LifeNew imaging technique catches DNA ‘blinking’ on
Dye-free imaging technique zooms in below 10-nanometer threshold, allowing new cellular views.
-
 Life
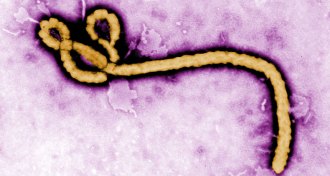
LifeRapid Ebola test to detect early infection in the works
Scientists are developing highly specific antibodies to detect Ebola sooner.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCold plasma puts the chill on norovirus
A new device uses cold plasma to kill foodborne pathogens.
-
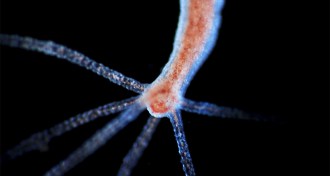 Animals
AnimalsHow hydras know where to regrow their heads
Regenerating pond animals called hydras inherit structural patterns from their original forms, researchers find.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsZika virus ‘spillback’ into primates raises risk of future human outbreaks
Spillback of Zika virus into monkeys may complicate eradication efforts.