News in Brief
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyIn Borneo, hunting emerges as a key threat to endangered orangutans
Only small numbers of Bornean orangutans will survive coming decades, researchers say.
By Bruce Bower -
 Plants
PlantsAncient ozone holes may have sterilized forests 252 million years ago
Swaths of barren forest may have led to Earth’s greatest mass extinction.
-
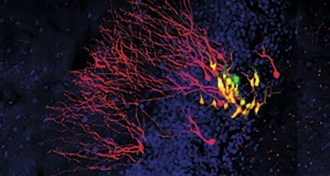 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWatch nerve cells being born in the brains of living mice
For the first time, scientists have seen nerve cells being born in the brains of adult mice.
-
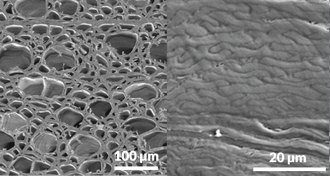 Materials Science
Materials ScienceSuperdense wood is lightweight, but strong as steel
New superdense wood could be a more lightweight, environmentally friendly alternative to current construction materials.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureGrapevines are more drought-tolerant than thought
Grapevines handle drought better than previously thought. This could inform irrigation management.
By Dan Garisto -
 Animals
AnimalsA killer whale gives a raspberry and says ‘hello’
Tests of imitating sounds finds that orcas can sort of mimic humans.
By Susan Milius -
 Environment
EnvironmentPlastic pollution increases risk of devastating disease in corals
Researchers estimate about 11 billion pieces of plastic are polluting Asia-Pacific corals, raising the risk of disease at scores of reefs.
By Dan Garisto -
 Astronomy
AstronomyThe X-ray glow keeps growing after the recent neutron star collision
X-rays from a neutron star collision have been getting brighter, and scientists are debating why.
-
 Earth
EarthVolume of fracking fluid pumped underground tied to Canada quakes
Study links volume of fracking fluid injected underground with hundreds of quakes in central Canada, and not the rate at which the fluids were injected.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomySpaceships could use blinking dead stars to chart their way
Timing signals from five pulsars allowed scientists to pinpoint an experiment’s place in space.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceShallow ice sheets discovered on Mars could aid future astronauts
Exposed water ice on steep Martian slopes suggest there’s a lot within a meter or two of the surface.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceHubble telescope ramps up search for Europa’s watery plumes
Astronomers are redoubling their efforts to confirm that the icy moon Europa spews water from its south pole.