News
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow Greenland sharks defy aging
When it comes to bucking the biological ails of aging, humans could learn something from Greenland sharks.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIt masquerades as malignant. But this bone-covered tumor is benign
Scientists have described a novel, yet benign bone-covered growth's characteristics for doctors, so patients don't receive unnecessary chemotherapy.
By Carly Kay -
 Space
SpaceSeismometers can track falling space junk
As the threat of falling spacecraft increases, using earthquake sensors to detect the effects of their sonic booms could better map trajectories.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA spot in the base of the brain has a love of language
Brain scans show a spot in the cerebellum attuned specifically to words, expanding on studies that point to the region's importance for language.
-
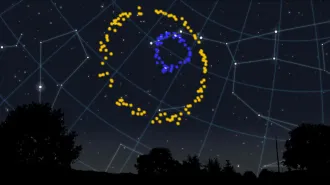 Cosmology
CosmologyA massive cosmic ring may challenge a key assumption about the universe
At 3.3 billion light-years across, the ring may challenge the “cosmological principle” that the universe looks uniform at sufficiently large scales.
- Anthropology
This hand stencil in Indonesia is now the oldest known rock art
The work suggests early Homo sapiens developed enduring artistic practices as they moved through the islands of Southeast Asia.
By Tom Metcalfe - Tech
This detached hand robot has a thing for skittering on its fingertips
The robot can bend, grasp and carry in ways humans can’t, which could help it navigate spaces too confined for human arms.
By Skyler Ware - Animals
This tool-using cow defies expectations for bovine braininess
Veronika the cow uses a brush as a tool to scratch herself, revealing rare problem-solving skills and expanding what we know of tool use in animals.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThis fish may play a hole in its head like a drum
The rockhead poacher is a little fish with a big pit in its head. The divot may be like a drum, making sound that rises above a chaotic, nearshore din.
By Jake Buehler -
 Earth
EarthA long-lost tectonic fragment may be shaking Northern California
Seismic tremors reveal a shallow fragment of an ancient tectonic plate beneath Northern California, helping explain damaging earthquakes near the surface.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineColor blindness hides a key warning sign of bladder cancer
A large U.S. health records study suggests that difficulty seeing blood in urine may put color-blind patients at higher risk.
By Elie Dolgin -
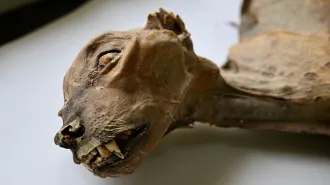 Animals
AnimalsHow cheetah mummies could help bring the species back to Arabia
Arabian cheetah mummies' DNA reveals that the long-lost population could be closely replaced by a cheetah population in northwestern Africa.
By Jake Buehler