Feature
-
 Animals
AnimalsYear in review: New dates, place proposed for dogs’ beginnings
This year’s dog research suggested older origins and a new location of domestication for man's best friend.
-
 Humans
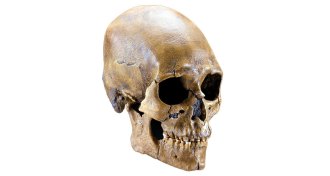
HumansYear in review: Native Americans are Kennewick kin
Ancient DNA identified 8,500-year-old Kennewick Man as a Native American relative.
By Bruce Bower -
 Genetics
GeneticsYear in review: Fluke extinction surprises lab
A die-off of bacteria in a carefully controlled lab experiment offered an evolutionary lesson this year: Survival depends not only on fitness but also on luck.
-
 Neuroscience
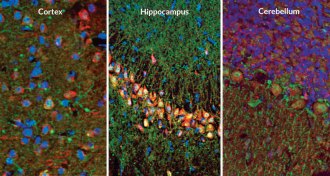
NeuroscienceYear in review: Gaps in brain nets might store memories
Holes in nets that surround nerve cells may store long-term memories, scientists proposed this year.
-
 Math
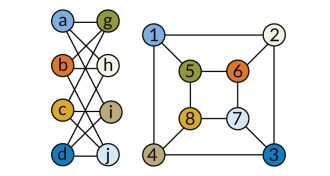
MathYear in review: New algorithm quickly spots identical networks
In what may be a once-in-a-decade advance, a computer scientist claimed to have devised an algorithm that efficiently solves the notorious graph isomorphism problem.
By Andrew Grant -
 Health & Medicine
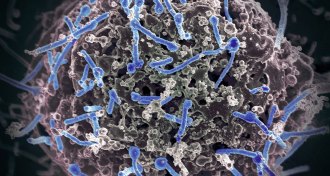
Health & MedicineYear in review: Ebola vaccines on the way
After more than a year of furiously developing and testing potential Ebola vaccines, two candidates have risen to the top and may soon be available for use.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Genetics
GeneticsGene drives spread their wings
Gene drives may wipe out malaria and take down invasive species. But they may be difficult to control.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsCan DNA predict a face?
DNA-based facial sketches are moving into the crime-solving arena. With current science, predictions of some features are better than others.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsGetting creative to cut methane from cows
Changing feed, giving vaccines and selective breeding may enable scientists to help beef and dairy cattle shake their title as one of society's worst methane producers.
By Laura Beil -
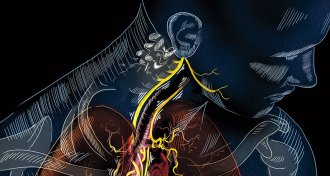 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceViva vagus: Wandering nerve could lead to range of therapies
Researchers are testing ways to stimulate the vagus nerve to treat a slew of ailments.
-
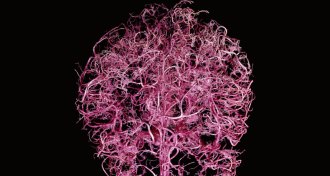 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBlood exerts a powerful influence on the brain
Instead of just responding to the energy needs of neurons, the blood can have a direct and powerful influence on the brain.
-
 Earth
EarthNew fascination with Earth’s ‘Boring Billion’
The Mesoproterozoic era, known as the boring billion, had very low oxygen, but it set the stage for the evolution of animals.