All Stories
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe odds of developing long COVID dropped as the coronavirus evolved
As different coronavirus variants took center stage during the pandemic, the chances of developing long COVID fell, especially for vaccinated people.
-
 Neuroscience
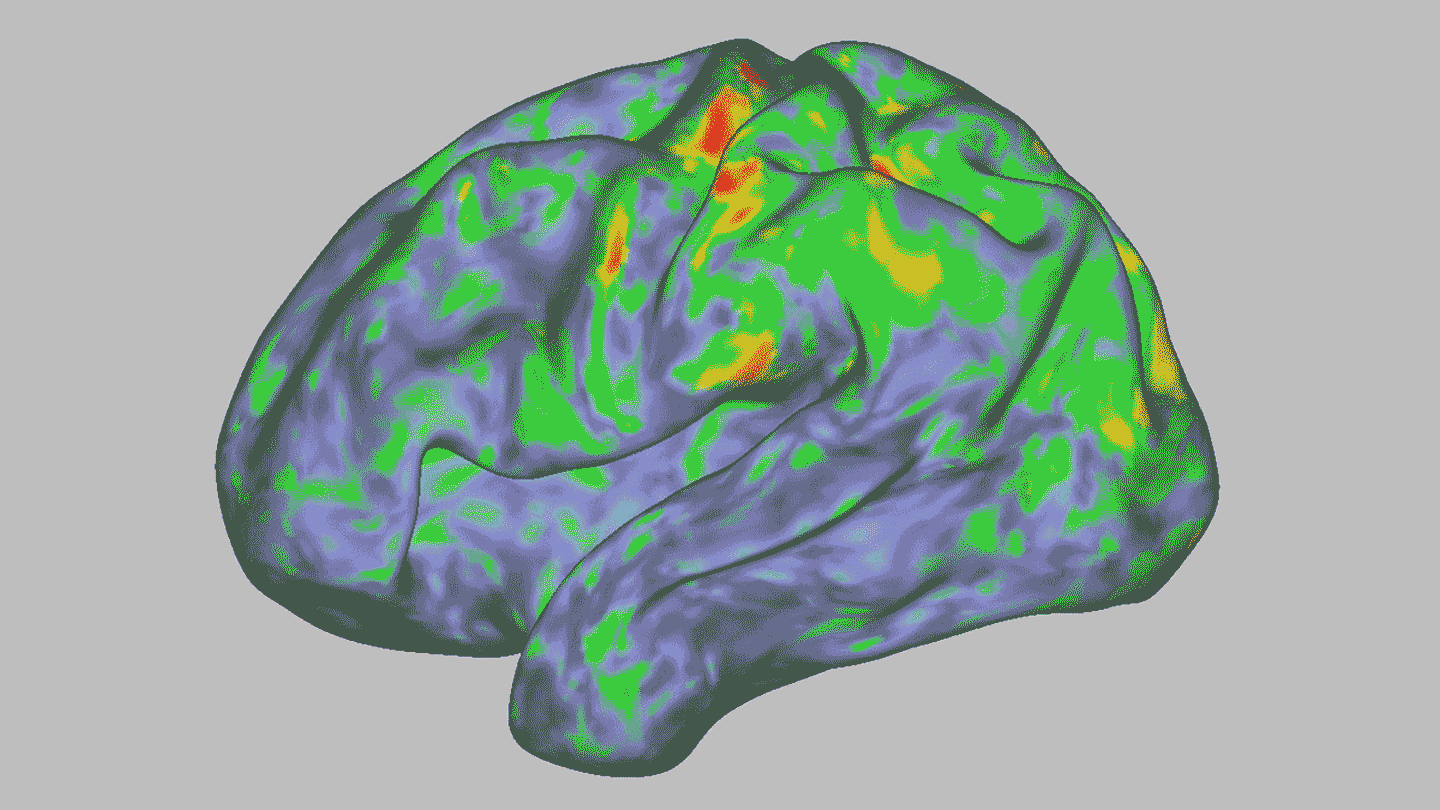
NeurosciencePsilocybin temporarily dissolves brain networks
A high dose of the psychedelic drug briefly throws the brain off kilter. Other, longer-lasting changes could hint at psilocybin's therapeutic effects.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceJupiter’s Great Red Spot may be less than 200 years old
An analysis of images spanning hundreds of years suggests a dark spot spied in the late 1600s and early 1700s is distinct from the Red Spot seen today.
-
 Health & Medicine
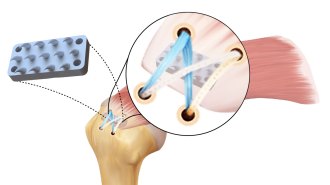
Health & MedicineThis python-inspired device could make rotator cuff surgeries more effective
A new device, modeled after a python’s teeth and grip, could double the strength of rotator cuff repairs and prevent retearing after surgery.
By Claire Yuan -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRogue antibodies may cause some long COVID symptoms
Tissue-targeting antibodies have been a key suspect in long COVID. Now, two studies show that antibodies from patients can cause symptoms in mice.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceSulfur was key to the first water on Earth
Hydrogen bonded with sulfur may have given our world its first water after the hydrogen broke away and joined with oxygen in the planet’s crust.
By Ken Croswell -
 Climate
ClimatePlants might not hold on to carbon as long as we thought
Radiocarbon from bomb tests reveals that plants store more carbon than previously estimated in leaves and stems, which are vulnerable to degradation.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceJurassic Park’s amber-preserved dino DNA is now inspiring a way to store data
DNA is capable of encoding all sorts of data. Storing it in an amberlike material may keep that information safe for nearly forever.
By Payal Dhar -

Striving to break the global grip of malnutrition
Editor in chief Nancy Shute discusses the quest for solutions in challenges such as childhood malnutrition, Andean bear conservation and assessing AI’s cognition.
By Nancy Shute -

-

‘Space hurricanes’ churn at both of Earth’s magnetic poles
The southern hemisphere’s ionosphere experiences about 23 space hurricanes per year, which is on par with the northern hemisphere.
-
 Humans
HumansWorld record speeds for two Olympics events have fallen over time. We can go faster
The human body can go faster in the 100-meter dash and the 50-meter freestyle. But to reach full potential, our technique must be perfect.