All Stories
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHow people suppress memories may be key to PTSD recovery
People who recovered from PTSD changed the way their brains handle intrusive thoughts, a study of survivors of the 2015 Paris terrorist attacks shows.
-
 Paleontology
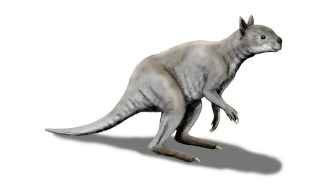
PaleontologyHumans, not climate change, may have wiped out Australia’s giant kangaroos
About 40,000 years ago, giant kangaroos vanished Down Under. Dental analyses suggest a varied diet, meaning climate change was not the main cause.
-
 Climate
ClimateCalifornia wildfire season should be over. So why is L.A. burning?
In some parts of California, fire season is now year-round due to rising heat and little rain. High winds and dry conditions are fueling L.A.’s infernos.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsCosmic rays could help reveal how tornadoes form
Subatomic particles called muons could measure pressure changes in supercell thunderstorms and the twisters they kick up.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMore new geckos have been found hiding in Southeast Asia’s limestone towers
Nearly 200 new gecko species found in living in karst landscapes reveal the rugged regions as dynamic areas of speciation.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPoop is on the menu for a surprising number of animals
A new tally finds dozens of species giving food a second go-round, from babies boosting their microbiomes to adults seeking easier-to-access nutrition.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIs alcohol linked to cancer? Here’s what the science says
A new U.S. Surgeon General's report describes the link between drinking alcohol and developing cancer. Many Americans aren’t aware of the risk.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat to know about the first bird flu–related death in the U.S.
H5N1 has infected 66 people in the United States since early 2024, mostly causing mild illness. A Louisiana man was the first to get severely sick.
-
 Animals
Animals‘Forever chemicals’ are causing health problems in some wildlife
Deformed scales in hatchlings and biomarkers indicative of disease progression are two health impacts on turtles at PFAS-polluted sites in Australia.
-
 Health & Medicine
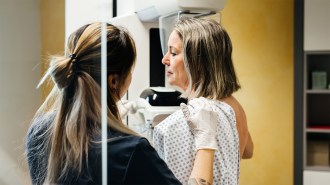
Health & MedicineAI helps doctors detect more breast cancer in the largest real-world study
AI is as good as clinicians at interpreting mammograms, a cancer study with nearly 500,000 participants in Germany suggests.
-
 Animals
AnimalsVelvet ants have the Swiss Army knife of venoms
A velvet ant bite like “hot oil from the deep fryer” delivers an array of peptides that inflicts pain on insects and mammals alike.
By Amanda Heidt -
 Planetary Science
Planetary SciencePluto may have captured its moon Charon with a kiss
When Pluto met Charon, there was an instant connection, new simulations suggest.