All Stories
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceExtreme gas loss dried out Mars, MAVEN data suggest
Over the planet’s history, the Martian atmosphere has lost 66 percent of its argon and a majority of its carbon dioxide, according to data from NASA’s MAVEN spacecraft.
-
 Paleontology
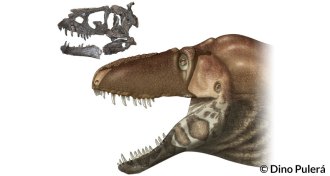
PaleontologyNew tyrannosaur had a sensitive side
Tyrannosaurs may have had sensitive snouts that detected temperature and touch.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFor kids, daily juice probably won’t pack on the pounds
An analysis of existing studies suggests that regular juice drinking isn’t linked to much weight gain in kids.
-
 Animals
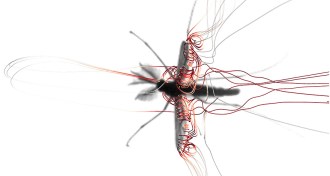
AnimalsMosquito flight is unlike that of any other insect
High-speed video and modeling reveal a more complex understanding of mosquito flight.
-
 Oceans
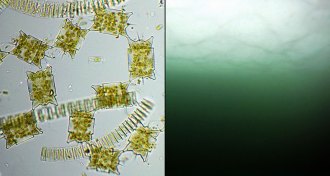
OceansThinning ice creates undersea Arctic greenhouses
Arctic sea ice thinned by climate change increasingly produces conditions favorable for phytoplankton blooms in the waters below, new research suggests.
-
 Anthropology
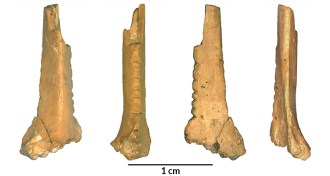
AnthropologyNeandertals had an eye for patterns
Neandertals carved notches in a raven bone, possibly to produce a pleasing or symbolic pattern, scientists say.
By Bruce Bower -
 Astronomy
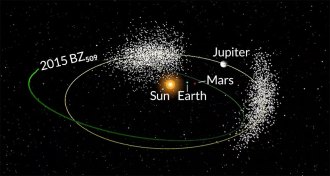
AstronomyAsteroid in Jupiter’s orbit goes its own way
Asteroid shares Jupiter’s orbit around the sun but travels in the opposite direction as the planet.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGene editing of human embryos yields early results
Gene editing in embryos has started in labs, but isn’t ready for the clinic.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSarcasm looks the same in the brain whether it’s words or emoji
Sarcasm via winking emoji affects the brain like verbal irony does.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomySupermassive black hole gets kicked to the galactic curb
Gravitational waves may have given a supermassive black hole a big kick, with enough energy to send it flying toward the edges of its host galaxy.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSpray-on mosquito repellents are more effective than other devices
To avoid mosquito bites, stick with spray-on repellents and skip the bracelets and citronella candles, a new study says.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDon’t put greasy Q-tips up your kid’s nose, and other nosebleed advice
Nosebleeds in children are common and usually nothing to fret about.