All Stories
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyEinstein’s light-bending by single far-off star detected
A measurement so precise Einstein thought it couldn't be done has demonstrated his most famous theory on a star outside the solar system for the first time.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineChoosing white or whole-grain bread may depend on what lives in your gut
Gut microbes determine how people’s blood sugar levels respond to breads.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBig slimy lips are the secret to this fish’s coral diet
A new imaging study reveals how tubelip wrasses manage to munch on stinging corals.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyScalding hot gas giant breaks heat records
KELT 9b’s sun blasts it with so much radiation that the planet’s dayside is hotter than most stars and its atmosphere is being stripped away.
-
 Life
LifeWhen it comes to the flu, the nose has a long memory
Mice noses have specialty immune cells with long memories.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSooty terns’ migration takes the birds into the path of hurricanes
Sooty terns migrate south from southern Florida and back again. The track sometimes takes the birds into the path of hurricanes, a new study finds.
-
 Earth
EarthAntarctica’s Larsen C ice shelf is within days of completely cracking
The crack in Antarctica’s Larsen C ice shelf grew another 17 kilometers between May 25 and May 31, 2017 and is at risk of breaking off a massive iceberg.
-
 Climate
ClimateU.S. will withdraw from climate pact, Trump announces
President Trump announced June 1 that the United States will withdraw from the Paris climate accord.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhen preventing HIV, bacteria in the vagina matter
Vaginal bacteria affect how well microbicide gels used to prevent HIV work.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrains encode faces piece by piece
Cells in monkey brains build up faces by coding for different characteristics.
-
 Physics
PhysicsLIGO snags another set of gravitational waves
Two black holes stirred up the third set of gravitational waves ever detected.
-
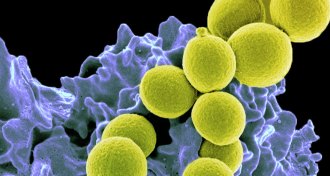 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, antibiotic resistance alarms went unheeded
Scientists have worried about antibiotic resistance for decades.