All Stories
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceSee the latest stunning views of Jupiter
Once every 53 days, NASA’s Juno spacecraft zooms past Jupiter’s cloud tops. A new sequence of images reveals the encounter from Juno’s viewpoint.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyAncient attack marks show ocean predators got scarier
Killer snails and other ocean predators that drill through shells have grown bigger over evolutionary time.
By Susan Milius -
 Earth
EarthMagma stored under volcanoes is mostly solid
Ancient zircon crystals provide clues about the magma that fuels volcanic eruptions.
-
 Quantum Physics
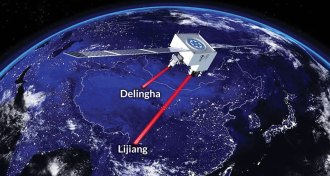
Quantum PhysicsQuantum satellite shatters entanglement record
A satellite sent entangled particles to two Chinese cities 1,200 kilometers apart.
-
 Health & Medicine
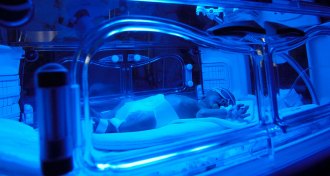
Health & MedicineIn 1967, researchers saw the light in jaundice treatment
Researchers discovered how to use light to treat babies with jaundice 50 years ago. But questions remain about the technique’s effectiveness in some cases.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFacial recognition changes a wasp’s brain
A new study maps genes at play in a paper wasp’s brain during facial recognition.
-
 Life
LifeHow bearded dragons switch their sex
RNA editing might affect reptile sex determination at temperature extremes.
-
 Health & Medicine
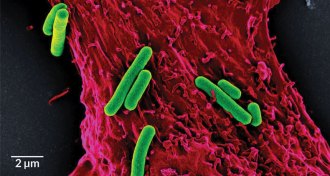
Health & MedicineNew heart attack treatment uses photosynthetic bacteria to make oxygen
Photosynthetic bacteria can produce oxygen to keep rat heart muscles healthy after a heart attack.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyLaunch your imagination with Science News stories
You don’t need a novel or a movie to escape into what feels like another reality. Just flip through the pages of Science News. The stories will take you to other worlds, as well as inner, hidden ones.
-
 Climate
ClimateReaders question climate’s freshwater effects
Warming lakes, windmills for the Arctic, mosquito control and more in reader feedback.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyLife might have a shot on planets orbiting dim red stars
The number of planets in the habitable zone of dim red suns, known as M dwarfs, is growing. They’re a good place to look for life.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyTop 10 discoveries about waves
Another gravitational wave detection reaffirms the importance of waves for a vast spectrum of physical processes and technologies.