All Stories
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThe solar system’s earliest asteroids may have all been massive
A team of astronomers says the original asteroids all came in one size: extra large.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyGiant armored dinosaur may have cloaked itself in camouflage
An armored dinosaur the size of a Honda Civic also wore countershading camouflage, a chemical analysis of its skin suggests.
-
 Life
LifeLight pollution can foil plant-insect hookups, and not just at night
Upsetting nocturnal pollinators has daylight after-effects for Swiss meadow flowers.
By Susan Milius -
 Climate
ClimateSouth Asia could face deadly heat and humidity by the end of this century
If climate change is left unchecked, simulations show extreme heat waves in densely populated agricultural regions of India and Pakistan.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyYour solar eclipse experience can help science
The Aug. 21 total solar eclipse offers a rare opportunity for crowdsourced data collection on a spectacular celestial phenomenon.
-
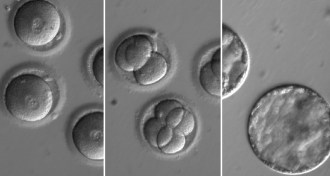 Genetics
GeneticsGene editing of human embryos gets rid of a mutation that causes heart failure
Gene editing of human embryos can efficiently repair a gene defect without making new mistakes.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsModern-day Alice trades looking glass for wormhole to explore quantum wonderland
A new paper shows how the possibility of wormholes linking quantum-entangled black holes could be tested in the laboratory.
-
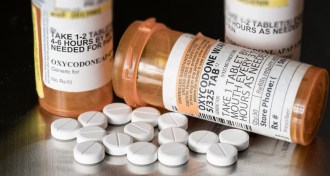 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOne in three U.S. adults takes opioids, and many misuse them
More than a third of U.S. adults used prescription opioids in 2015, and nearly 13 percent of that group misused the painkillers in some way.
By Kate Travis -
 Physics
PhysicsVirgo detector joins LIGO in the search for gravitational waves
The Virgo detector near Pisa, Italy, has begun searching for subtle ripples in the fabric of spacetime.
-
 Plants
PlantsA new portrait of the world’s first flower is unveiled
A reconstruction of the first flowers suggests the ancient blooms were bisexual.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOne in three U.S. adults takes opioids, and many misuse them
More than a third of U.S. adults used prescription opioids in 2015, and nearly 13 percent of that group misused the painkillers in some way.
By Kate Travis -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceEvidence mounts for an ocean on early Venus
Not long after its birth, Venus may have rocked a water ocean, new simulations suggest.