All Stories
-
 Artificial Intelligence
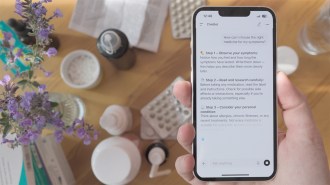
Artificial IntelligenceReal-world medical questions stump AI chatbots
Subtle shifts in how users described symptoms to AI chatbots led to dramatically different, sometimes dangerous medical advice.
-
 Oceans
OceansEvolution didn’t wait long after the dinosaurs died
New plankton arrived just a few millennia — maybe even decades — after the Chicxulub asteroid, forcing a rethink of evolution's catastrophe response speed.
By Elie Dolgin -
 Animals
AnimalsA sea turtle boom may be hiding a population collapse
In Cape Verde, conservation has boosted the sea turtle population 100-fold — but the male-female balance is way off.
-
Crossword: Copy That!
Solve the crossword from our March 2026 issue, in which we work on our code-switching.
By Rena Cohen -
 Astronomy
AstronomyThis inside-out planetary system has astronomers scratching their heads
A rocky exoplanet in the LHS 1903 system defies planet formation models, hinting that gravitational upheaval reshaped the red dwarf’s four worlds.
By Adam Mann -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA simple shift in schedule could make cancer immunotherapy work better
A lung cancer trial bolsters a long-held idea that treatment timing matters, showing a simple shift could help immunotherapy work better and extend lives.
By Elie Dolgin -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThis baby sling turns sunlight into treatment for newborn jaundice
A student created a low-cost baby carrier that filters sunlight to safely treat jaundice where electricity and equipment are scarce.
By Elie Dolgin -
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsFood chains in Caribbean coral reefs are getting shorter
Shorter food chains could mean reefs are less able to weather changes in food availability, threatening an already vulnerable ecosystem.
-
 Physics
PhysicsA precise proton measurement helps put a core theory of physics to the test
After years of confusion, a new study confirms the proton is tinier than once thought. That enables a test of the standard model of particle physics.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyFossilized vomit reveals 290-million-year-old predator’s diet
The regurgitated material from before the time of dinosaurs provides a rare window into the feeding habits of a prehistoric hunter.
By Jay Bennett -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAntibiotics can treat appendicitis for many patients, no surgery needed
After 10 years, just over half the people in a trial of antibiotics for appendicitis have not needed an appendectomy.
-
 Earth
EarthEarth’s core may hide dozens of oceans of hydrogen
Hydrogen reserves in Earth’s core large enough to supply at least nine oceans may influence processes on the surface today.
By Nikk Ogasa