All Stories
-
 Life
LifeEmbryos kill off male tissue to become female
Female embryos actively dismantle male reproductive tissue, a textbook-challenging study suggests.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHow an itch hitches a ride to the brain
Scientists have figured out how your brain registers the sensation of itch.
-
 Astronomy
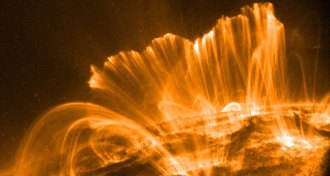
AstronomyWhy are the loops in the sun’s atmosphere so neat and tidy?
Observations during the total solar eclipse may explain why the sun’s atmosphere is so organized despite arising from a tangled magnetic field.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA new tool could one day improve Lyme disease diagnosis
There soon could be a way to differentiate between Lyme disease and a similar tick-associated illness.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGiant larvaceans could be ferrying ocean plastic to the seafloor
Giant larvaceans could mistakenly capture microplastics, in addition to food, in their mucus houses and transfer them to the seafloor in their feces.
-

-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineProtect little ones’ eyes from the sun during the eclipse
Pay attention to eye safety for kids during the solar eclipse.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyWhat can the eclipse tell us about the corona’s magnetic field?
The corona’s plasma jumps and dances thanks to the magnetic field, but scientists have never measured the field directly.
-
 Earth
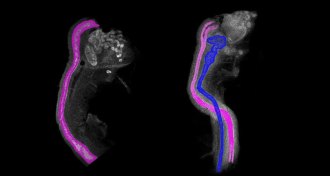
EarthSeismologists get to the bottom of how deep Earth’s continents go
Scientists may have finally pinpointed the bottoms of the continents.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThese spiders crossed an ocean to get to Australia
The nearest relatives of an Australian trapdoor spider live in Africa. They crossed the Indian Ocean to get to Australia, a new study suggests.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyCan the eclipse tell us if Einstein was right about general relativity?
During the eclipse, astronomers will reproduce the 1919 experiment that confirmed Einstein’s general theory of relativity.
-
 Particle Physics
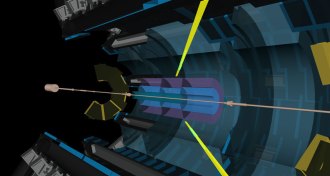
Particle PhysicsNormally aloof particles of light seen ricocheting off each other
Scientists spot evidence of photons interacting at the Large Hadron Collider.