All Stories
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyThese are the most-read Science News stories of 2017
From Cassini and eclipses to ladybugs and dolphins, Science News online readers had a wide variety of favorite stories on our website.
-
 Science & Society
Science & Society2017 delivered humility, and proved our potential
Acting Editor in Chief Elizabeth Quill reflects on some of the top scientific stories of 2017.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyColliding neutron stars, gene editing, human origins and more top stories of 2017
A gravitational wave discovery is the year's biggest science story — again.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThis year’s neutron star collision unlocks cosmic mysteries
A rare and long-awaited astronomical event united thousands of astronomers in a frenzy of observations.
-
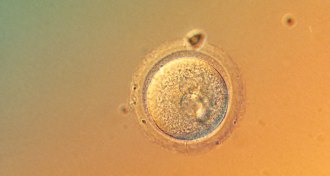 Genetics
GeneticsCRISPR gene editing moved into new territory in 2017
Scientists edited viable human embryos with CRISPR/Cas9 this year.
-
 Climate
ClimateThe Larsen C ice shelf break has sparked groundbreaking research
The hubbub over the iceberg that broke off Larsen C may have died down, but scientists are just getting warmed up to study the aftermath.
-
 Humans
HumansThe story of humans’ origins got a revision in 2017
Human evolution may have involved the gradual assembly of scattered skeletal traits, fossils of Homo naledi and other species show.
By Bruce Bower -
 Astronomy
AstronomySeven Earth-sized planets entered the spotlight this year
The discovery of seven Earth-sized planets orbiting a single cool star fuels a debate over what counts as good news in the search for life outside the solar system.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsA quantum communications satellite proved its potential in 2017
Quantum communication through space is now possible, putting the quantum internet within closer reach.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWorries grow that climate change will quietly steal nutrients from major food crops
Studies show that rice, wheat and other staples could lose proteins and minerals, putting more people at risk of hunger worldwide.
By Susan Milius -
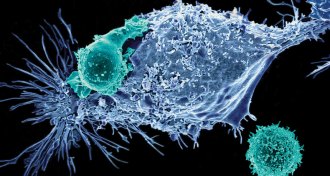 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineApproval of gene therapies for two blood cancers led to an ‘explosion of interest’ in 2017
The first gene therapies approved in the United States are treating patients with certain types of leukemia and lymphoma.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrains of former football players showed how common traumatic brain injuries might be
Examinations of NFL players’ postmortem brains turned up chronic traumatic encephalopathy in 99 percent of samples in large dataset.