All Stories
-
 Genetics
GeneticsCicadas on different schedules can hybridize
A new genetic study suggests that cicadas that emerge every 17 years have swapped genetic material with those that emerge every 13 years.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyClosing the gender gap in some science fields may take over 100 years
In some STEM fields, the gender gap won’t disappear for decades or even centuries, a new study suggests.
By Kyle Plantz -
 Climate
ClimateHeat waves are roasting reefs, but some corals may be resilient
The latest research on coral reefs clarifies the devastation of heat waves and looks at how coral might be able to adapt to warming waters.
By Dan Garisto -
 Astronomy
AstronomyCelebrity names now mark places on Pluto’s moon Charon
Pluto’s largest moon, Charon, now has 12 new names for its topological features.
By Dan Garisto -
 Life
LifeLarger spleens may help ‘sea nomads’ stay underwater longer
The Bajau people of Southeast Asia have a gene variant associated with larger spleens, boosting their oxygen while breath-hold diving, researchers say.
-
 Climate
ClimateRising CO2 levels might not be as good for plants as we thought
A 20-year experiment spots a reversal in the way two kinds of plants take up extra carbon from the atmosphere.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMale fruit flies enjoy ejaculation
Red light exposure made some genetically engineered fruit flies ejaculate, spurring a surge of a brain reward compound — and less desire for booze.
By Susan Milius -
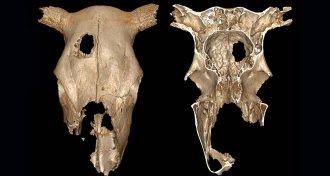 Anthropology
AnthropologyA hole in an ancient cow’s skull could have been surgery practice
Before performing skull operations on people, ancient surgeons may have rehearsed on cows.
By Bruce Bower -
 Microbes
MicrobesThis plastic-gobbling enzyme just got an upgrade
Scientists tweaked a bacterial enzyme and made it more efficient in breaking down plastics found in polyester and plastic bottles.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyNASA’s TESS spacecraft launches to begin its exoplanet search
After reaching its orbit in about two months, the telescope will start scanning nearby stars telltale dips in light that signal a passing planet.
-
 Physics
PhysicsHow ravens caused a LIGO data glitch
Ravens pecking at frosty pipes caused a glitch in gravitational wave data.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceThis meteorite’s diamonds hint that it was born in a lost planet
Bits of metal nestled inside diamonds suggest the space rock could have formed in a Mars-sized protoplanet in the early solar system.