All Stories
-
 Life
LifeBiologists are one step closer to creating snake venom in the lab
Milking snakes for venom may soon no longer be needed to make antidotes for bites.
-
 Tech
TechA new way to turn saltwater fresh can kill germs and avoid gunk buildup
A new device that harnesses sunlight to produce pure vapor from seawater could last longer and produce cleaner water than other technology.
-
 Climate
ClimateThe list of extreme weather caused by human-driven climate change grows
The tally of extreme weather events linked to climate change continues to grow, with new studies outlining links to more than a dozen events in 2017.
-
 Life
LifeGetting goose bumps could boost hair growth
The same nerves and muscles that create goose bumps may make hair grow.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceNASA’s OSIRIS-REx finds signs of water on the asteroid Bennu
NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft found signs of water and lots of boulders on the asteroid Bennu.
-
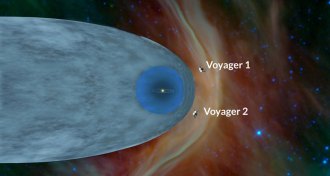 Cosmology
CosmologyVoyager 2 spacecraft enters interstellar space
Voyager 2 just became the second probe ever to enter interstellar space, and the first with a working plasma instrument.
-
 Physics
PhysicsA satellite screw-up reaffirms Einstein’s theory of gravity
Two spacecraft confirm that time passes more slowly closer to Earth’s surface.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyThese are our favorite science books of 2018
Science News writers and editors pick which science books were this year’s must-reads.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceMagnets make a new soft metamaterial stiffen up in a flash
Scientists can dial the stiffness of a bizarre new type of synthetic material up or down using magnets.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA gut-brain link for Parkinson’s gets a closer look
Early evidence suggests that Parkinson’s may be a gut disease that affects the brain.
By Laura Beil -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTwo new books explore the science and history of the 1918 flu pandemic
One-hundred years after the Spanish flu, ‘Pandemic 1918’ and ‘Influenza’ provide a new look at the global outbreak.
-
 Climate
ClimateGlobal carbon dioxide emissions will hit a record high in 2018
Carbon dioxide emissions from China, the United States and India all rose this year, a new report finds.