All Stories
-
 Animals
AnimalsThis spider’s barf is worse than its bite
Most spider species subdue dinner by injecting venom from their fangs. Feather-legged lace weavers swathe prey in silk, then upchuck a killing brew.
By Susan Milius -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAt early ages, autism in girls and boys looks similar
A new study of more than 2,500 children under 5 found little difference in autism symptoms between boys and girls.
-
 Space
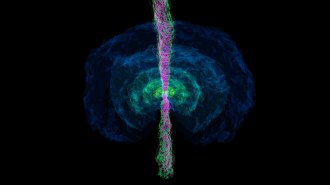
SpaceHere’s how a collision of star remnants launches a gleaming jet
A computer simulation shows how two neutron stars of unequal mass merge, form a black hole and spit out a jet of high energy matter.
-
 Physics
PhysicsRainbows of sound are a reality thanks to a new device
A plastic structure separates white noise into pitches, like a rainbow splits light into colors, offering a novel way to manipulate sound.
-
 Computing
ComputingThere’s no cheating this random number generator
From jury duty to tax audits, randomness plays a big role. Scientists used quantum physics to build a system that ensures those number draws can’t be gamed.
By Celina Zhao -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow one mom is navigating vaccines’ uncertain future
With CDC upheaval, new limits on who can get some vaccines and an ongoing measles outbreak, parents like me face unfamiliar hurdles to protecting our kids.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyA 43,000-year-old Neandertal fingerprint has been found in Spain
An ochre dot in Spain may hold one of the oldest, most complete Neandertal fingerprints, hinting at symbolic behavior in our ancient relatives.
-
 Earth
EarthClimate change is coming for your cheese
Adapting to climate change by replacing grass in cows' feed with corn affected the nutritional value and quality of cheese, French researchers found.
-
 Physics
PhysicsHow to get the biggest splash at the pool using science
Move over belly flops and cannonballs. Manu jumps, pioneered by New Zealand’s Māori and Pasifika communities, reign supreme.
By Elie Dolgin -
 Humans
HumansFDA cuts imperil food safety, but not how you might think
Layoffs at the FDA, USDA and CDC could erode the U.S. food safety system. Experts aren’t so worried about milk or chicken today; they’re concerned about the future.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Planetary Science
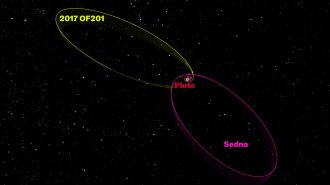
Planetary ScienceA possible new dwarf planet skirts the solar system’s edge
For the dwarf planet candidate, one trip around the sun takes over 24,000 years. Its orbit challenges a proposed path for a hypothetical Planet Nine.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA cup of chickpeas a day lowers cholesterol
Adding a cup of chickpeas or black beans to people’s daily diets could improve health by lowering cholesterol and inflammation, a new study suggests.
By Meghan Rosen