All Stories
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyA toe bone hints that Neandertals used eagle talons as jewelry
An ancient eagle toe bone elevates the case for the use of symbolic bird-of-prey pendants among Neandertals, researchers say.
By Bruce Bower -
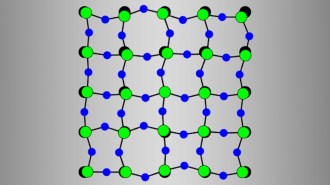 Chemistry
ChemistryMolecular jiggling may explain why some solids shrink when heated
Scientists may have figured out how scandium fluoride crystals shrink as temperature rises, possibly leading to new insights into superconductors.
By Sofie Bates -
 Animals
AnimalsApple TV+’s ‘The Elephant Queen’ shies away from hard truths
The Elephant Queen offers an intimate look into the lives of elephants, but the documentary largely avoids threats the animals face.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew details on immune system ‘amnesia’ show how measles causes long-term damage
Measles wipes the memories of immune cells in the body.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSleep may trigger rhythmic power washing in the brain
Strong, rhythmic waves of cerebrospinal fluid wash into the human brain during sleep and may help clean out harmful proteins.
-
 Life
LifeVampire bat friendships endure from captivity to the wild
Vampire bats can form social bonds that persist from a lab setting to the outdoors, suggesting the cooperative relationships are like friendships.
-
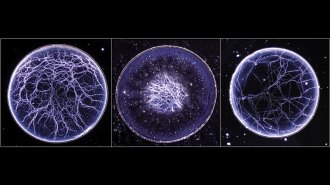 Chemistry
ChemistryAmerican whiskeys leave unique ‘webs’ when evaporated
If you don’t have a sophisticated palate, it turns out you can distinguish among bourbons with a microscope.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyAlaska’s free money for residents hints at how universal basic income may work
Since 1982, Alaskans have gotten an annual oil dividend. Scientists say that program hints at the pros and cons of a universal basic income.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Animals
AnimalsSpider webs don’t rot easily and scientists may have figured out why
Spider silk doesn’t rot quickly because bacteria can’t access its nitrogen, a nutrient needed for the microbes’ growth, scientists say.
-
 Climate
ClimateA new estimate triples the number of people in the path of rising seas
Sea level rise could flood coastal areas now home to 340 million to 480 million people by 2100, with Asia most affected, a study finds.
By Sofie Bates -
 Life
LifeSaharan silver ants are the world’s fastest despite relatively short legs
Saharan silver ants can hit speeds of 108 times their body length per second.
By Susan Milius -
 Space
SpaceRules guarding other planets from contamination may be too strict
Voluntary international guidelines for visiting the moon, Mars and other places — and for bringing stuff back to Earth — are overly cautious, scientists say.