All Stories
-
 Health & Medicine
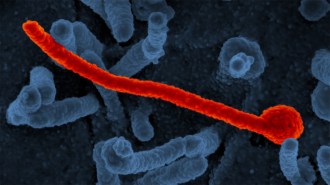
Health & MedicineA new antiviral blocks 6 deadly viruses in mice but faces a long road ahead
Scientists report that targeting sugars on virus surfaces stopped multiple infections, though the approach needs much refinement before human trials.
By Payal Dhar -
 Microbes
MicrobesWhat makes chocolate taste so good? It’s the microbes
Beans matter, but microbes may be the real secret to fine chocolate flavor. Scientists are building starter cultures that may improve quality.
-
 Earth
EarthUseful metals get unearthed in U.S. mines, then they’re tossed
Recovering these metals from mining by-products destined for waste sites could offset the need to import them from elsewhere or open new mines.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineElderly cats with dementia may hold clues for Alzheimer’s
Immune cells in aging cat brains with amyloid beta destroy nerve endings, mimicking the progression of Alzheimer’s disease in humans.
-
 Health & Medicine
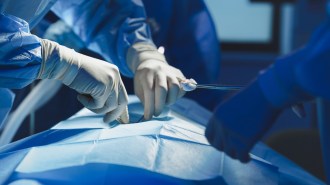
Health & MedicineScientists perform the first pig-to-human lung transplant
The genetically modified lung remained viable for nine days, but the recipient’s immune responses need more research, scientists say.
By Skyler Ware -
 Animals
AnimalsThe mysterious, extinct ‘Fuegian dog’ was actually a semi-tame fox
Historic European accounts long described the canids as domesticated dogs. A new study suggests that’s probably not true.
By Jake Buehler -

Seeing the world in new ways
Editor in Chief Nancy Shute examines the exciting potential of the new Vera C. Rubin Observatory and muses on the mesmerizing world of fractals.
By Nancy Shute - Planetary Science
NASA’s Webb telescope spotted a new moon orbiting Uranus
Like Uranus's other 28 moons, the newfound object spotted by JWST will be named after a William Shakespeare or Alexander Pope character.
-
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial IntelligenceCan fake faces make AI training more ethical?
Demographic bias gaps are closing in face recognition, but how training images are sourced is becoming the field’s biggest privacy fight.
By Celina Zhao -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineShifting vaccine guidelines inject uncertainty into getting fall COVID shots
Respiratory viruses often surge in the fall. We asked an infectious diseases expert how best to protect ourselves given a shifting vaccine landscape.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe phoenix isn’t the only critter to survive the flames
There are no real phoenixes hiding anywhere. But science has revealed that some living things can take quite a bit of heat.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAround the world, birds sing longer in light-polluted areas
In light-polluted landscapes, birds' singing time is an average of 50 minutes longer per day. It's still unclear if this hurts bird health or helps.
By Jake Buehler