All Stories
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsWildfires launch microbes into the air. How big of a health risk is that?
How does wildfire smoke move bacteria and fungi — and what harm might they do to people when they get there?
By Megan Sever -
 Animals
AnimalsDiscarded COVID-19 PPE such as masks can be deadly to wildlife
From entanglements to ingestion, two biologists are documenting the impact of single-use masks and gloves on animals around the world.
-
 Oceans
OceansCorals’ hidden genetic diversity corresponds to distinct lifestyles
Observation and DNA analysis expose identical reef corals as distinct species with unique ecologies, suggesting much greater coral biodiversity.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow researchers can keep birds safe as U.S. wind farms expand
Tracking bald eagle abundance and migrating whooping cranes provides a clearer picture of where wind turbines could be safely built.
By Jack J. Lee -
 Climate
ClimateA trek under Thwaites Glacier’s ice shelf reveals specific risks of warm water
An underwater autonomous craft collected the first data on the chemistry of seawater eroding the icy underbelly of Antarctica’s Thwaites Glacier.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyA record-breaking, oxygen-starved galaxy may be full of gigantic stars’ shrapnel
The newly discovered galaxy may have once been home to stars more than 300 times as massive as the sun — a peek at conditions in the early universe.
By Ken Croswell -
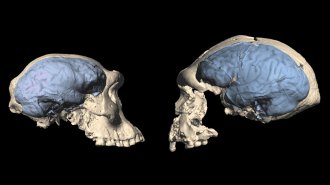 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient humans may have had apelike brains even after leaving Africa
Modern humanlike brains may have evolved surprisingly late, about 1.7 million years ago, a new study suggests.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsHow matter’s hidden complexity unleashed the power of nuclear physics
In the last century, physicists learned to split atomic nuclei and revealed a complex world of fundamental particles.
-
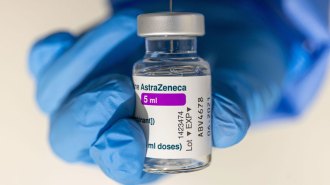 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAstraZeneca’s COVID-19 vaccine is tied to uncommon blood clots in rare cases
Blood clots should be listed as a possible side effect of AstraZeneca’s vaccine, but its benefits still outweigh the risks, experts say.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyPeople add by default even when subtraction makes more sense
People default to addition when solving puzzles and problems, even when subtraction works better. That could underlie some modern-day excesses.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsMuon magnetism could hint at a breakdown of physics’ standard model
After two decades, a new measurement of the muon magnetic anomaly reinforces earlier hints that its value disagrees with standard physics.
-
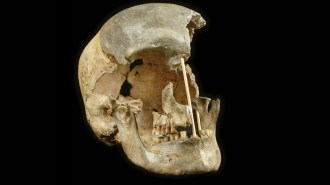 Genetics
GeneticsEurope’s oldest known humans mated with Neandertals surprisingly often
DNA from ancient fossils suggests interbreeding regularly occurred between the two species by about 45,000 years ago, two studies find.
By Bruce Bower