All Stories
-
 Animals
AnimalsThis ‘ghost shark’ has teeth on its forehead
Spotted ratfish, or “ghost sharks,” have forehead teeth that help them grasp onto mates. It’s the first time teeth have been found outside of a mouth.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceLung cancer plugs into the mouse brain
Exploring the relationship between cancer cells and nerve cells, which can signal tumors to grow, could unearth ways to slow disease.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceEnceladus’ ocean may not have produced precursor chemicals for life
Building blocks of life have been found on this moon of Saturn. They may come from chemical reactions beyond Enceladus’ possible life-supporting ocean.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyAn ancient reptile’s fossilized skin reveals how it swam like a seal
A reptile fossil is the first of its kind with skin and partially webbed feet, possibly showing how later species like plesiosaurs adapted to water.
-

When cancer targets the young
Editor in Chief Nancy Shute discusses the troubling rise of cancer among younger adults, and shares a glimmer of hope for those diagnosed in early childhood.
By Nancy Shute -
 Humans
HumansStaying on the keto diet long term could carry health risks
Months on a high-fat keto diet put mice at risk for cardiovascular disease and impaired insulin secretion.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsA primordial black hole may have spewed the highest energy neutrino ever found
The Big Bang may have spawned these theoretical black holes, whose lives are thought to end in a burst of extremely energetic particles.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBats live with some viruses. But others can do them in
Bats can carry some deadly human pathogens without signs of illness. A new survey shows that other viruses can still be bad for bats.
-
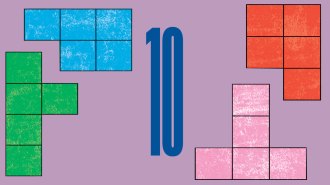
Math puzzle: The four islands
Solve the math puzzle from our October 2025 issue, in which four princesses divide up lands to keep peace.
By Ben Orlin -
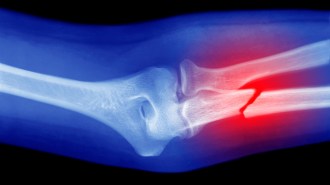 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA handheld ‘bone printer’ shows promise in animal tests
Demonstrated in rabbits, the 3-D printer might someday print bone grafts directly onto fractures, complete with antibiotics to ease healing.
By Payal Dhar -
 Animals
AnimalsTug or fetch? Some dogs sort toys by how they are used
Dogs that easily learn the names of toys might also mentally sort them by function, a new example of complex cognitive activity in the canine brain.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy are so many young people getting cancer?
Diagnoses for several cancers before age 50 have been increasing rapidly since the 1990s. Scientists don’t know why, but they have a few suspects.