All Stories
- Physics
These simple knife tricks stop onion tears instantly
With a high-speed camera and a tiny guillotine, scientists showed that chopping onions slowly and with sharper knives cuts down on tears.
By Carly Kay -
 Climate
ClimateAustralia’s tropical forests now emit CO₂, clouding the COP30 talks
These tropical forest CO₂ emissions may warn of similar shifts in other regions, a key topic for COP30 climate talks in Brazil.
-
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial IntelligenceA conference just tested AI agents’ ability to do science
AI promises to speed up scientific analysis and writing. However, AI agents struggled with accuracy and judgment.
-
 Humans
HumansNapoleon’s retreating army may have been plagued by these microbes
DNA from Napoleonic soldiers’ teeth uncovered two fever-causing bacteria that may have worsened the army’s fatal retreat from Russia.
By Meghan Rosen -
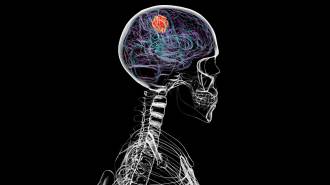 Humans
HumansBrain cancer can dissolve parts of the skull
Glioblastoma doesn't just affect the brain. It also erodes bones in the skull and changes the composition of immune cells in skull marrow.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsSubway mosquitoes evolved millennia ago in ancient Mediterranean cities
A variety of subway-dwelling mosquito seems like a modern artifact. But genomic analysis reveals the insect got its evolutionary start millennia ago.
By Jake Buehler -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyDinosaurs were thriving before the asteroid hit, new analysis suggests
New dating of New Mexico rocks suggest diverse dinosaurs thrived there just before the impact, countering the idea dinos were already on their way out.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryCoffee beans pooped out by civets really are tastier. Here’s why
Pricey civet coffee gets its cred from its journey through the mammal’s gut, which changes the content of fat, protein, fatty acids — and even caffeine.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhich venomous snakes strike the fastest?
Vipers have the fastest strikes, but snakes from other families can give some slower vipers stiff competition.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsQuantum ‘echoes’ reveal the potential of Google’s quantum computer
Google says its quantum computer achieved a verifiable calculation that classic computers cannot. The work could point to future applications.
-
 Animals
AnimalsScientists and fishers have teamed up to find a way to save manta rays
Thousands of at-risk manta and devil rays become accidental bycatch in tuna fishing nets every year. A simple sorting grid could help save them.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMost women get uterine fibroids. This researcher wants to know why
Biomedical engineer Erika Moore investigates diseases that disproportionately affect women of color.