All Stories
-
 Humans
HumansAncient southern Africans took genetic evolution in a new direction
An ancient, shared set of human-specific genes underwent changes in a geographically isolated population after around 300,000 years ago, scientists say.
By Bruce Bower -
 Earth
EarthHuman-caused earthquakes are real. Here’s why even stable regions can snap
Human activity can cause “healed” faults to release their stored strength, triggering unexpected quakes in tectonically stable regions.
-
 Physics
PhysicsTwisted stacks of 2-D carbon act like a weird type of superconductor
“Magic-angle” graphene may provide new clues into poorly understood unconventional superconductors, which operate at higher-than-normal temperatures.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSelf-hypnosis with cooling mental imagery could ease hot flashes
Postmenopausal women who listened to self-guided hypnosis recordings daily for six weeks saw meaningful improvements in hot flash symptoms.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePersonalized ‘prehabilitation’ helps the body brace for major surgery
A small study finds that individualized prehab can dampen harmful immune responses and may reduce complications after an operation.
By Anna Gibbs -
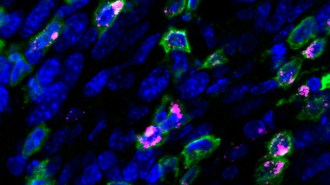 Humans
HumansA therapeutic HPV vaccine shrank cervical tumors in mice
An HPV vaccine delivered into the nose can treat cervical tumors in mice. The vaccine targets a cancer protein produced by the virus.
By Meghan Rosen -
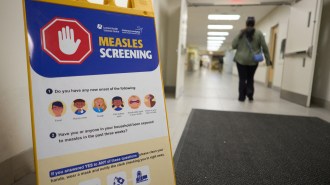 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCanada just lost its measles elimination status. Is the U.S. next?
Canada has had more than a year of continuous measles transmission. The United States has until January to limit cases before losing status.
-
 Climate
ClimateHere are 3 big ideas to combat climate change, with or without COP
As action from the U.N.’s huge COP30 international meeting falls short, smaller groups are banding together to find ways to fight climate change.
By Meghie Rodrigues and Carolyn Gramling -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceListen to the crackle of Martian ‘mini-lightning’
A microphone on NASA’s Perseverance rover recorded the sounds of electrical discharges generated by dusty gusts.
By Nikk Ogasa -
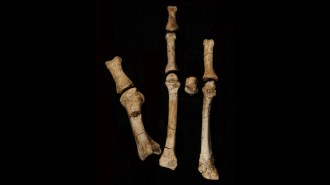 Anthropology
AnthropologyA foot fossil suggests a second early human relative lived alongside Lucy
Foot bones and other fossils have been attributed to Australopithecus deyiremeda, a recently discovered species that may shake up the human family tree.
By Jay Bennett -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyGratitude can increase joy, even if it feels a little cringe
Like exercise, gratitude takes many forms. Finding the right practice, research shows, is up to the individual.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Animals
AnimalsCuddly koalas had a brutal, blade-toothed close cousin
Ancient collagen preserved in the bones of extinct Australian mammals is revealing their evolutionary relationships, leading to some surprises.
By Jake Buehler