All Stories
-
 Animals
Animals50 years ago, scientists wondered how birds find their way home
In the 1970s, lab tests hinted that birds can navigate using magnetic fields. New studies suggest that beak and eye proteins are behind the ability.
-

-

Rethinking how we live with wildfires
Editor in chief Nancy Shute discusses a new approach for managing wildfires that includes collaboration with local and Indigenous communities.
By Nancy Shute -
 Math
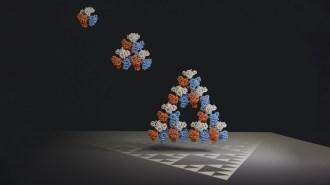
MathScientists find a naturally occurring molecule that forms a fractal
The protein assembles itself into a repeating triangle pattern. The fractal seems to be an accident of evolution, scientists say.
-
 Animals
AnimalsIn a first, these crab spiders appear to collaborate, creating camouflage
Scientists found a pair of mating crab spiders blending in with a flower. The report may be the first known case of cooperative camouflage in spiders.
-
 Life
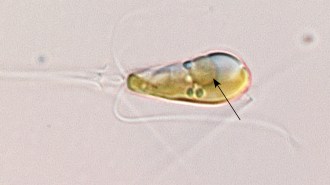
LifeThis marine alga is the first known eukaryote to pull nitrogen from air
An alga’s bacterial symbiote has evolved into an organelle that turns atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, making the alga unique among eukaryotes.
By Jake Buehler -
 Space
Space50 years ago, scientists found a lunar rock nearly as old as the moon
Studies of such rocks continue to reveal secrets about the moon’s history.
-
 Space
SpaceHow a sugar acid crucial for life could have formed in interstellar clouds
Computer calculations and lab experiments have revealed a possible mechanism for the creation of glyceric acid, which has been seen in meteorites.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTeens are using an unregulated form of THC. Here’s what we know
The compound is called delta-8-THC and, like delta-9-THC in marijuana, comes from the cannabis plant and may hurt teens’ brains.
-
 Health & Medicine
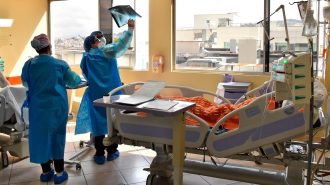
Health & MedicineImmune cells’ intense reaction to the coronavirus may lead to pneumonia
Immune cells that patrol lung tissue may play a role in the progression of a coronavirus infection to pneumonia, lab studies show.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyWhat Science News saw during the solar eclipse
Science News staffers took to different parts of the United States to take in the eclipse’s glow. Here’s a glimpse of what we saw during the 2024 event.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsFlowers may be big antennas for bees’ electrical signals
The finding suggests a way for plants to share information about nearby pollinators and communicate when to trigger nectar production.