All Stories
-
 Life
LifeIt’s a big year for cicadas. Here’s what to know about this year’s emergence
Periodical cicadas are an odd marvel of nature. This year, the biggest brood of all is coming out in the U.S. South while another emerges in the Midwest.
By Susan Milius -
 Climate
ClimateWarm water is sneaking underneath the Thwaites Glacier — and rapidly melting it
The salty water, just 3.6 degrees Celsius above the ice’s melting point, is undermining the foundation of the Antarctic glacier.
By Douglas Fox -
 Animals
AnimalsA built-in pocket protector keeps sawfish from ‘sword fighting’ in the womb
What’s to prevent pups, with a snout that resembles a hedge trimmer, from slicing and dicing each other in mom’s uterus? Scientists have the answer.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsScientists propose a hunt for never-before-seen ‘tauonium’ atoms
Made of heavy relatives of the electron, the exotic atoms could be used to test the theory of quantum electrodynamics.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePrivacy remains an issue with several women’s health apps
Inconsistent privacy policies and dodgy data collection in popular fertility and pregnancy tracking apps put women’s health information at risk.
By Payal Dhar -
 Space
SpaceHere’s how predictions of the sun’s corona during the 2024 eclipse fared
Models from Predictive Science Inc. forecasted the appearance of the sun’s corona during the April eclipse to better understand our star.
By Adam Mann -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMalnutrition’s effects on the body don’t end when food arrives
Children may struggle with inflammation, a weakened immune system and gut problems. New treatments may repair some damage.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceVenus might be as volcanically active as Earth
Data from NASA’s Magellan spacecraft suggest that volcanic activity is widespread on Venus.
By Adam Mann -
 Space
SpaceForget moon walking. Scientists want to give moon running a try
Researchers took over an amusement park attraction to test out an idea for how astronauts might exercise on the moon.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial IntelligenceReinforcement learning AI might bring humanoid robots to the real world
Reinforcement learning techniques could be the keys to integrating robots — who use machine learning to output more than words — into the real world.
-
 Neuroscience
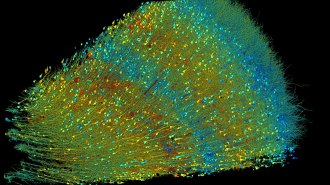
NeuroscienceBiological puzzles abound in an up-close look at a human brain
Mirror-image nerve cells, tight bonds between neuron pairs and surprising axon swirls abound in a bit of gray matter smaller than a grain of rice.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsTwo real-world tests of quantum memories bring a quantum internet closer to reality
Scientists successfully entangled quantum memories linked by telecommunications fibers across two different urban environments.