All Stories
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyA distant quasar may be zapping all galaxies around itself
Star formation has ceased within at least 16 million light-years of the quasar. A similar phenomenon may have fried the Milky Way when it was young.
By Ken Croswell -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyThe asteroid that may have killed the dinosaurs came from beyond Jupiter
The Chicxulub crater, left behind by the impact, contains elemental traces that suggest the origins of the notorious projectile.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentMore than 4 billion people may not have access to clean water
The new estimate, based on data from 135 low- and middle-income countries, is more than double the World Health Organization’s official count.
By Claire Yuan -
 Space
SpaceAstronauts actually get stuck in space all the time
Butch Wilmore and Sunita Williams join more than a dozen astronauts who’ve been stranded in space by mechanics, weather or geopolitics since the 1970s.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy mpox is a global health emergency — again
The WHO made the declaration as a potentially more infectious version of the deadly virus has emerged and mpox cases are rapidly rising across Africa.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA hunger protein reverses anorexia symptoms in mice
Boosting levels of protein ACBP spurred the mice to eat and gain weight. It is unclear if any drugs based on the protein might help people with anorexia.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyStonehenge’s mysterious Altar Stone had roots in Scotland
New analyses indicate that this weighty piece of the site’s architecture, once thought to come from Wales, was somehow moved at least 750 kilometers.
By Bruce Bower -
 Space
SpaceScientists want to send endangered species’ cells to the moon
Climate change is threatening Earth’s biodiversity banks. It might be time to build a backup on the moon.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNasty-tasting cane toads teach crocodiles a lifesaving lesson
After tasting nausea-inducing toad butts, crocodiles in Australia learned to avoid the poisonous live version. Crocodile deaths dropped by 95 percent.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYour medications might make it harder for you to beat the heat
Chronic illnesses and the medications that treat them may make it harder to handle extreme heat. It’s even harder to study how.
-
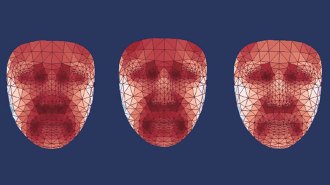 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYour face’s hot spots may reveal how well you are aging
If facial heat maps prove effective at picking up signs of chronic diseases such as diabetes, they could become another health assessment tool.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA risk-tolerant immune system may enable house sparrows’ wanderlust
Birds that are willing to eat seed spiked with chicken poop have higher expression levels of a gut immunity gene, a new study finds.