All Stories
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyA large fossil leg bone hints at T. rex’s origins, but scientists disagree
A new analysis of a large fossil shinbone suggests T. rex ancestors came from North America instead of Asia. Not everyone agrees.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsWhy African striped mice can be the best of dads — or the worst
Environmental cues can flip a molecular switch in the brain, turning males from caregivers to killers.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAI may be giving teens bad nutrition advice
AI-generated meal plans for fictional teens cut an entire meal’s worth of calories and carbs while overemphasizing protein and fats, a new study reports.
By Lily Burton -
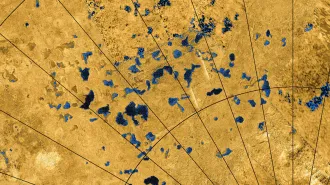 Space
SpaceOne possible recipe for life on Titan is a bust
An experiment mimicking conditions on the Saturn moon suggests that cell-like bubbles don’t form in methane lakes, puncturing hopes for alien life.
-
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial IntelligenceAI auto-complete may subtly shape views on social issues
People are increasingly using AI auto-complete features when writing. Unbeknownst to them, that feature may change how they think.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Genetics
GeneticsThe Amazon molly — a sex-skipping fish — hacks evolution
The Amazon molly reproduces without sex. A genomic copy-and-paste trick called gene conversion may explain how it avoids evolutionary meltdown.
By Elie Dolgin -
 Astronomy
AstronomyA strange ‘chirp’ in a brilliant stellar blast points to a magnetar
Superluminous supernovas are the brightest stellar explosions in the universe. Astronomers may have found a mechanism that can trigger these events.
By Jay Bennett -
 Animals
AnimalsSubmerged bumblebee queens breathe underwater
Submerged bees breathe and use strategies that don’t require oxygen, lab tests show. In nature, that trick could help the bees survive floods.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine‘Smart underwear’ measures how often humans fart
“Zen digesters” rarely fart. “Hydrogen hyperproducers” fart a lot. Scientists are investigating what is typical.
-
 Plants
PlantsTree tops sparkle with electricity during thunderstorms
Ultraviolet cameras captured faint electrical flashes from leaves and branches as storm charges built up in the atmosphere.
By Lily Burton -
 Climate
ClimateLakes are growing in Alaska. That’s not entirely a bad thing
Alaska’s glacial lakes are growing as glaciers retreat out of basins. These lakes will change desolate glacial rivers into thriving salmon habitat.
By Douglas Fox -
 Physics
PhysicsWhen the pressure’s off, this superconductor appears to break records
A sudden release of pressure allowed a copper-based compound to superconduct at the highest temperature yet for atmospheric pressure, a study claims.