All Stories
-
 Climate
ClimateLakes are growing in Alaska. That’s not entirely a bad thing
Alaska’s glacial lakes are growing as glaciers retreat out of basins. These lakes will change desolate glacial rivers into thriving salmon habitat.
By Douglas Fox -
 Physics
PhysicsWhen the pressure’s off, this superconductor appears to break records
A sudden release of pressure allowed a copper-based compound to superconduct at the highest temperature yet for atmospheric pressure, a study claims.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow does early pregnancy lower breast cancer risk? Odd cells could offer clues
Suspicious cells build up in mice that haven’t given birth, a new study finds. They could help explain a longstanding mystery of breast cancer biology.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceNASA’s DART spacecraft changed an asteroid’s orbit around the sun
A 2022 NASA mission changed the orbit of the asteroid Dimorphos around its companion. New data shows their joint orbit around the sun also changed.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceThe remarkable brains of ‘SuperAgers’ hold clues about how we age
A new study reports signs that nerve cells in the brain keep dividing over the decades. It’s not so simple.
- Tech
Robots with fingernails can grasp thin edges
A robotic hand with fingernail-like tips lets robots peel fruit, open lids and pick up thin, flat objects with more precise, human-like dexterity.
By Ananya -
 Animals
AnimalsA koala population’s rapid rebound may let it escape inbreeding’s perils
As koalas in southern Australia have grown from a few hundred to almost half a million, the marsupials show signs of regaining lost genetic variation.
By Jake Buehler -
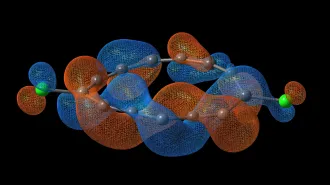 Chemistry
ChemistryThis molecule puts a new twist on the Möbius strip
A molecule made of carbon and chlorine is half as twisty as the paper loops common in math classes.
-
 Plants
PlantsChickpeas can grow in moon dirt and make seeds
Chickpeas produced seeds in simulated lunar soil, offering clues for future space farming.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceA Titan collision may link Saturn’s tilt, its moon Hyperion and its rings
A new study proposes that a crash between Titan and another moon spawned Hyperion and, much later, destabilized Saturn’s inner moons into rings.
-
 Climate
ClimateHundreds of studies have missed how much the oceans are rising
A widely used method to calculate sea level rise may have missed up to a century of change, so the risks could hit home for millions sooner than thought.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceA chemical ‘Goldilocks zone’ may limit which planets can host life
Life needs nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus. But without the right balance of oxygen, these elements get locked away in planets’ cores.